Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(M1130-09-57) Development of a Gefitinib-Loaded Niosomal Formulation for Pulmonary Delivery via Nebulization
Monday, November 10, 2025
11:30 AM - 12:30 PM CT
- SH
Sheng-Min Huang
PhD Student
National Taiwan University
Taipei, New Taipei, Taiwan (Republic of China) 
Wei-Ren Ke, PhD
Assistant Professor
National Taiwan University
Taipei City, Taipei, Taiwan (Republic of China)- CC
Chieh-Sheng Cheng, MS
Chief Executive Officer
HCmed Innovations Co., Ltd
Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan (Republic of China) - HC
Henry Cuevas Brun, MS
Business Department Director & Senior Aerosol Scientist
HCmed Innovations Co., Ltd
Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan (Republic of China)
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. Gefitinib, an oral epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor, is widely used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but its efficacy is limited by first-pass metabolism and systemic distribution, leading to poor drug accumulation in lung tumors. Niosomes are nanocarriers with bilayer membrane structures formed from non-ionic surfactants, offering high stability, low toxicity, and low production cost. Encapsulating gefitinib in niosomes improves solubility and stability, optimizing biodistribution and pharmacokinetics. Pulmonary delivery via inhalation provides a non-invasive, localized route enabling direct lung deposition, bypassing hepatic metabolism, and reducing systemic side effects. Nebulizers generate aerosolized droplets for deep lung delivery, offering precise dosing, ease of use, and efficient absorption. This study aims to develop a gefitinib-loaded niosomal formulation for nebulization to achieve targeted pulmonary delivery and provide a novel administration strategy for gefitinib.
Methods: A three-factor and three-level Box-Behnken design (BBD), a design of experiments (DOE) approach, was employed to optimize the gefitinib-loaded niosomal formulations prepared via the ethanol injection method. Gefitinib, cholesterol, and the non-ionic surfactant Span 60 were dissolved in absolute ethanol as the organic phase. This solution was gradually injected into pH 7.4 phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) using a syringe pump at a controlled flow rate of 0.05 mL/min under continuous stirring. The critical quality attributes (CQAs), including stirring rate, ethanol-to-PBS volume ratio, and span 60-to-cholesterol molar ratio, were systematically varied across 15 runs according to the BBD framework. Resulting niosomal dispersions were purified by dialysis to remove unencapsulated drug and residual solvent. Subsequently, the niosome particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency (EE), and drug loading (DL) were measured. A response surface model was developed using the BBD data to predict optimal formulation parameters. Following optimization, the selected niosomal formulation was evaluated using vibrating mesh nebulizers (VMC; Pulmogine, HCmed, Taipei, Taiwan) with three mesh pore sizes. The effects of nebulization parameters on aerosol performance and niosome integrity were investigated. Integrity assessments were performed by collecting nebulized droplets via condensation in a collector and comparing the niosome properties before and after nebulization. Aerosol performance was further assessed using a cooled Next Generation Impactor (NGI) operated at a flow rate of 15 L/min, determining aerodynamic particle size distribution (APSD).
Results: The BBD was used to investigate the effect of stirring rate, Span 60-to-cholesterol molar ratio, and ethanol-to-PBS volume ratio on critical quality attributes (Table 1). Among the tested variables, the Span 60-to-cholesterol ratio significantly influenced particle size and EE. Higher Span 60 content increased membrane fluidity, leading to vesicle destabilization, drug leakage, and larger particle size. In contrast, increased stirring rates effectively reduced particle size by promoting formation of smaller, more uniform vesicles. After optimization, the niosomes were evaluated for structural integrity and aerosolization performance using vibrating mesh nebulizers (Figure 1). Pre- and post-nebulization characterization showed significant yet subtle changes in particle size and zeta potential (~5 nm increase and ~3 mV change, respectively, across three mesh sizes), indicating minimal impact on niosome structural performance after aerosolization. However, an apparent reduction in EE was observed across all mesh pore sizes, with the least loss in the large mesh (small: 14.5 ± 1.8%, median: 13.3 ± 3.1%, large: 8.9 ± 3.7%), suggesting less impact on niosomal integrity during nebulization. Additionally, increasing mesh pore size shortened nebulization time (small: 197.3 ± 11.0, median: 166.7 ± 7.1, large: 128.0 ± 6.1, p < 0.05) and improved aerosol output (small: 0.61 ± 0.03, median: 0.72 ± 0.03, large: 0.94 ± 0.04, p < 0.05). Aerosol performance (Table 2) revealed that emitted dose (%) increased with mesh size (small: 34.9 ± 4.3, median: 43.5 ± 5.5, large: 47.6 ± 11.8, p = 0.22), whereas fine particle dose (FPD) decreased with increasing mesh size (small: 15.8 ± 4.5, median: 20.0 ± 8.6, large: 8.2 ± 3.3, p = 0.12), likely due to larger droplets. Notably, the mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric standard deviation (GSD) remained within suitable ranges for pulmonary deposition, supporting the potential of gefitinib-loaded niosomes for lung delivery across various nebulizer configurations.
Conclusion: This study successfully developed and optimized a gefitinib-loaded niosomal formulation for nebulization. Using the ethanol injection method with BBD optimization, the formulation achieved desirable niosome properties, including small particle size, narrow size distribution, and high encapsulation efficiency. The optimized niosomes maintained structural integrity after nebulization, with acceptable changes in particle size, PDI, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency. Aerodynamic characterization confirmed MMAD and GSD values within the suitable range for inhalation. Larger mesh sizes increased aerosol output and produced larger droplets, thereby reducing FPD. Overall, these findings support the feasibility of niosomal formulations for nebulization and inhalation, providing a promising strategy for targeted pulmonary delivery of gefitinib while potentially reducing systemic exposure and associated side effects.
References: 1. Freddie Bray, Mathieu Laversanne, Hyuna Sung et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024, 74, 229-63.
2. Deepak Nagdiya, Manish Kumar, Sanchit Arora et al. Drug delivery systems of gefitinib for improved cancer therapy: A review. OpenNano. 2023, 14, 100183.
3. Sergio Liga, Cristina Paul, Elena-Alina Moacă et al. Niosomes: composition, formulation techniques, and recent progress as delivery systems in cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2024, 16, 223.
4. Mohamad Saimi NI, Salim N, Ahmad N, Abdulmalek E, et al. Aerosolized Niosome formulation containing gemcitabine and cisplatin for lung cancer treatment: optimization, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2021, 13(1), 59.
5. Jana Szabová, Ondrej Mišík, Jan Fučík et al. Liposomal form of erlotinib for local inhalation administration and efficiency of its transport to the lungs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2023, 634, 122695.
Acknowledgements: This research was supported by the provision of the Pulmogine® nebulizer from HCmed Innovations Co., Ltd.
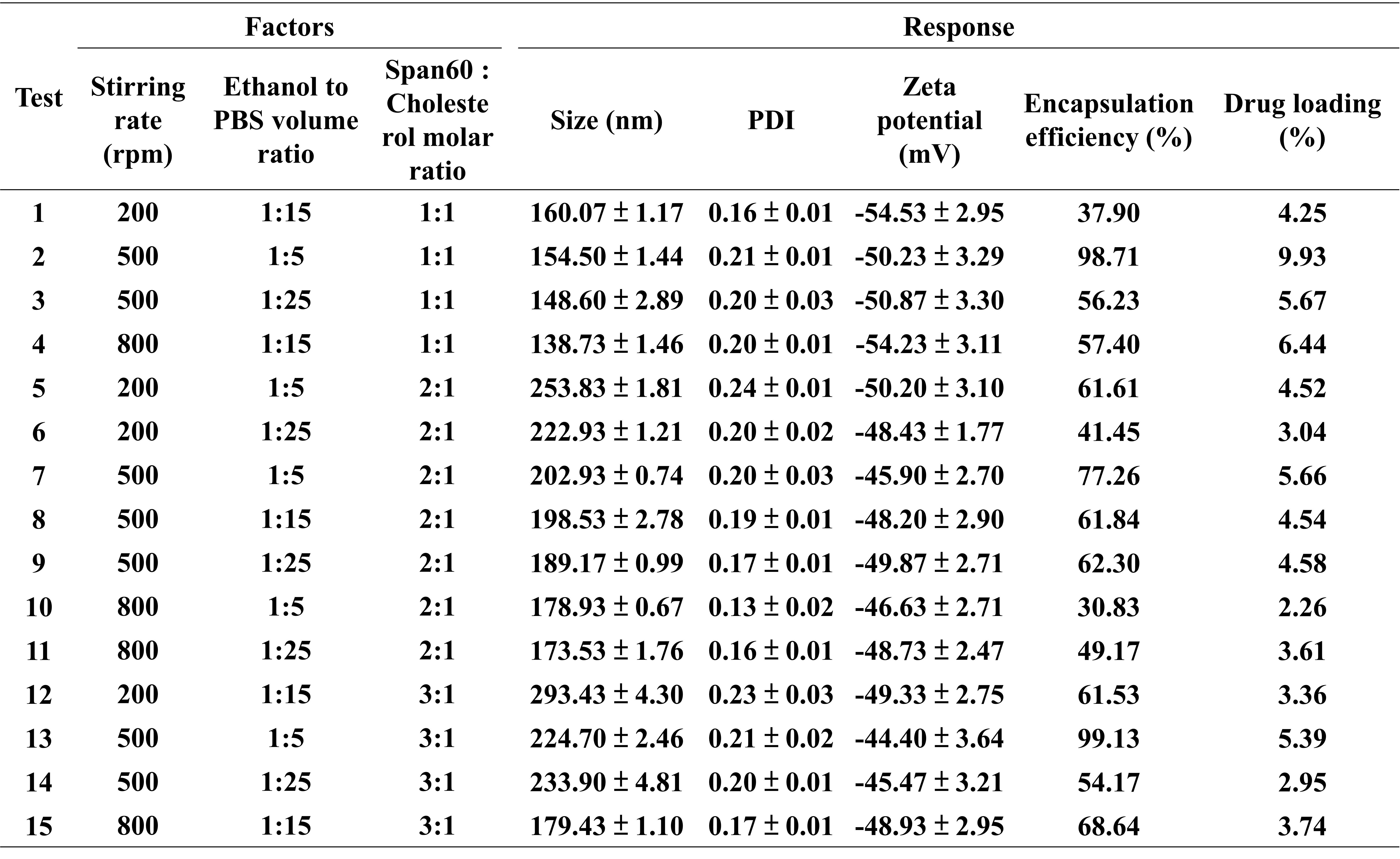 Table 1. The Box-Behnken design matrix for the development of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes, comprising combinations of three levels and three factors. The measured responses included particle size, PDI, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and drug loading (n = 3).
Table 1. The Box-Behnken design matrix for the development of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes, comprising combinations of three levels and three factors. The measured responses included particle size, PDI, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and drug loading (n = 3).
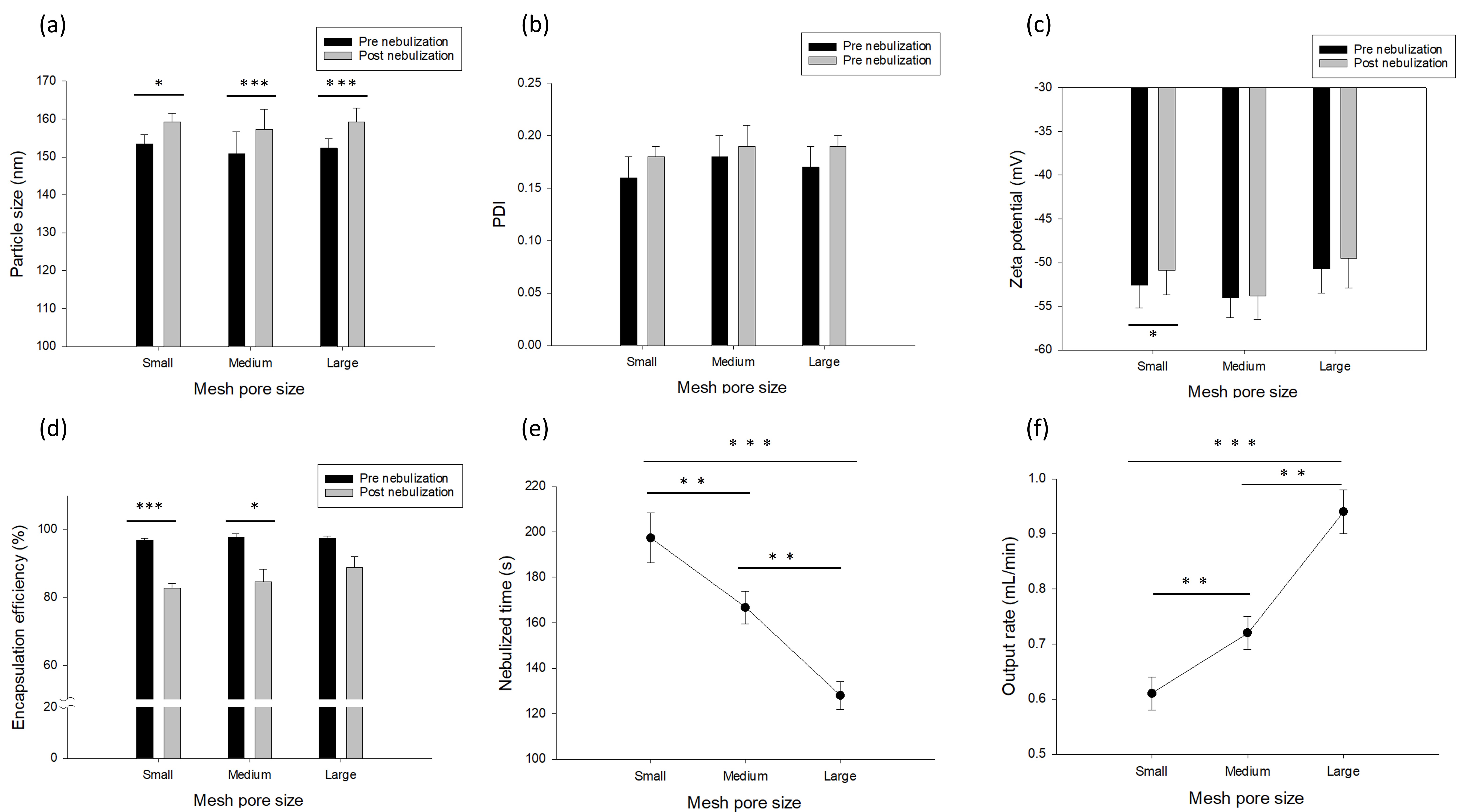 Figure 1. Physicochemical properties of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes before and after nebulization using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes (small, medium, and large). The evaluated parameters included particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, nebulization time, and output rate. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-test (α = 0.05) and one way ANOVA, with significance indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 1. Physicochemical properties of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes before and after nebulization using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes (small, medium, and large). The evaluated parameters included particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, nebulization time, and output rate. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-test (α = 0.05) and one way ANOVA, with significance indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
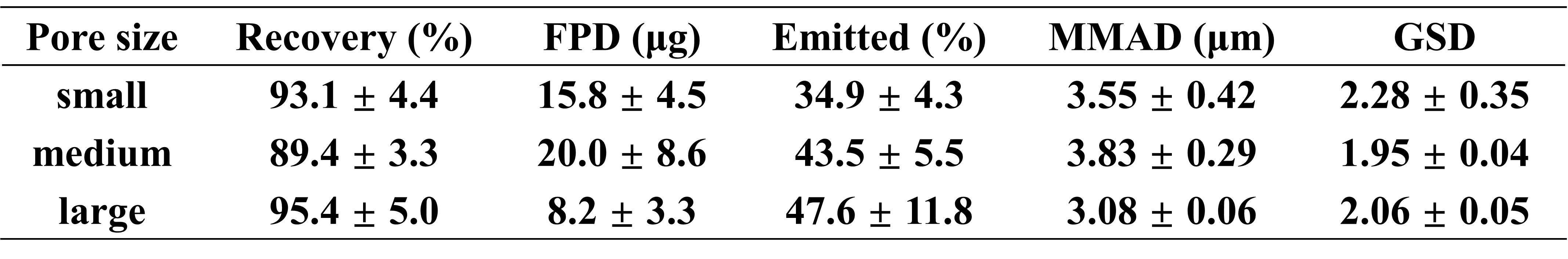 Table 2. Aerodynamic Particle Size Distribution (APSD) parameters of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes. Parameters include recovery, fine particle dose (FPD), emitted dose, emitted %, mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric standard deviation (GSD). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
Table 2. Aerodynamic Particle Size Distribution (APSD) parameters of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes. Parameters include recovery, fine particle dose (FPD), emitted dose, emitted %, mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric standard deviation (GSD). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
Methods: A three-factor and three-level Box-Behnken design (BBD), a design of experiments (DOE) approach, was employed to optimize the gefitinib-loaded niosomal formulations prepared via the ethanol injection method. Gefitinib, cholesterol, and the non-ionic surfactant Span 60 were dissolved in absolute ethanol as the organic phase. This solution was gradually injected into pH 7.4 phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) using a syringe pump at a controlled flow rate of 0.05 mL/min under continuous stirring. The critical quality attributes (CQAs), including stirring rate, ethanol-to-PBS volume ratio, and span 60-to-cholesterol molar ratio, were systematically varied across 15 runs according to the BBD framework. Resulting niosomal dispersions were purified by dialysis to remove unencapsulated drug and residual solvent. Subsequently, the niosome particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency (EE), and drug loading (DL) were measured. A response surface model was developed using the BBD data to predict optimal formulation parameters. Following optimization, the selected niosomal formulation was evaluated using vibrating mesh nebulizers (VMC; Pulmogine, HCmed, Taipei, Taiwan) with three mesh pore sizes. The effects of nebulization parameters on aerosol performance and niosome integrity were investigated. Integrity assessments were performed by collecting nebulized droplets via condensation in a collector and comparing the niosome properties before and after nebulization. Aerosol performance was further assessed using a cooled Next Generation Impactor (NGI) operated at a flow rate of 15 L/min, determining aerodynamic particle size distribution (APSD).
Results: The BBD was used to investigate the effect of stirring rate, Span 60-to-cholesterol molar ratio, and ethanol-to-PBS volume ratio on critical quality attributes (Table 1). Among the tested variables, the Span 60-to-cholesterol ratio significantly influenced particle size and EE. Higher Span 60 content increased membrane fluidity, leading to vesicle destabilization, drug leakage, and larger particle size. In contrast, increased stirring rates effectively reduced particle size by promoting formation of smaller, more uniform vesicles. After optimization, the niosomes were evaluated for structural integrity and aerosolization performance using vibrating mesh nebulizers (Figure 1). Pre- and post-nebulization characterization showed significant yet subtle changes in particle size and zeta potential (~5 nm increase and ~3 mV change, respectively, across three mesh sizes), indicating minimal impact on niosome structural performance after aerosolization. However, an apparent reduction in EE was observed across all mesh pore sizes, with the least loss in the large mesh (small: 14.5 ± 1.8%, median: 13.3 ± 3.1%, large: 8.9 ± 3.7%), suggesting less impact on niosomal integrity during nebulization. Additionally, increasing mesh pore size shortened nebulization time (small: 197.3 ± 11.0, median: 166.7 ± 7.1, large: 128.0 ± 6.1, p < 0.05) and improved aerosol output (small: 0.61 ± 0.03, median: 0.72 ± 0.03, large: 0.94 ± 0.04, p < 0.05). Aerosol performance (Table 2) revealed that emitted dose (%) increased with mesh size (small: 34.9 ± 4.3, median: 43.5 ± 5.5, large: 47.6 ± 11.8, p = 0.22), whereas fine particle dose (FPD) decreased with increasing mesh size (small: 15.8 ± 4.5, median: 20.0 ± 8.6, large: 8.2 ± 3.3, p = 0.12), likely due to larger droplets. Notably, the mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric standard deviation (GSD) remained within suitable ranges for pulmonary deposition, supporting the potential of gefitinib-loaded niosomes for lung delivery across various nebulizer configurations.
Conclusion: This study successfully developed and optimized a gefitinib-loaded niosomal formulation for nebulization. Using the ethanol injection method with BBD optimization, the formulation achieved desirable niosome properties, including small particle size, narrow size distribution, and high encapsulation efficiency. The optimized niosomes maintained structural integrity after nebulization, with acceptable changes in particle size, PDI, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency. Aerodynamic characterization confirmed MMAD and GSD values within the suitable range for inhalation. Larger mesh sizes increased aerosol output and produced larger droplets, thereby reducing FPD. Overall, these findings support the feasibility of niosomal formulations for nebulization and inhalation, providing a promising strategy for targeted pulmonary delivery of gefitinib while potentially reducing systemic exposure and associated side effects.
References: 1. Freddie Bray, Mathieu Laversanne, Hyuna Sung et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024, 74, 229-63.
2. Deepak Nagdiya, Manish Kumar, Sanchit Arora et al. Drug delivery systems of gefitinib for improved cancer therapy: A review. OpenNano. 2023, 14, 100183.
3. Sergio Liga, Cristina Paul, Elena-Alina Moacă et al. Niosomes: composition, formulation techniques, and recent progress as delivery systems in cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2024, 16, 223.
4. Mohamad Saimi NI, Salim N, Ahmad N, Abdulmalek E, et al. Aerosolized Niosome formulation containing gemcitabine and cisplatin for lung cancer treatment: optimization, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2021, 13(1), 59.
5. Jana Szabová, Ondrej Mišík, Jan Fučík et al. Liposomal form of erlotinib for local inhalation administration and efficiency of its transport to the lungs. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2023, 634, 122695.
Acknowledgements: This research was supported by the provision of the Pulmogine® nebulizer from HCmed Innovations Co., Ltd.
 Table 1. The Box-Behnken design matrix for the development of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes, comprising combinations of three levels and three factors. The measured responses included particle size, PDI, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and drug loading (n = 3).
Table 1. The Box-Behnken design matrix for the development of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes, comprising combinations of three levels and three factors. The measured responses included particle size, PDI, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and drug loading (n = 3). Figure 1. Physicochemical properties of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes before and after nebulization using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes (small, medium, and large). The evaluated parameters included particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, nebulization time, and output rate. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-test (α = 0.05) and one way ANOVA, with significance indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 1. Physicochemical properties of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes before and after nebulization using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes (small, medium, and large). The evaluated parameters included particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, nebulization time, and output rate. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-test (α = 0.05) and one way ANOVA, with significance indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Table 2. Aerodynamic Particle Size Distribution (APSD) parameters of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes. Parameters include recovery, fine particle dose (FPD), emitted dose, emitted %, mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric standard deviation (GSD). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
Table 2. Aerodynamic Particle Size Distribution (APSD) parameters of Gefitinib-loaded niosomes using mesh nebulizers with different pore sizes. Parameters include recovery, fine particle dose (FPD), emitted dose, emitted %, mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) and geometric standard deviation (GSD). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).