Bioanalytics - Biomolecular
(M1330-01-06) Challenges in Developing LC-MS/MS and LC-UV Methods for Modified MicroRNAs: A Case Study of Two RNA Mimics and an Inhibitor with Antiasthmatic Potential
- AS
Anna Siemiątkowska, PhD, MSc
Assistant Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - AS
Anna Siemiątkowska, PhD, MSc
Assistant Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - MK
Marta Karaźniewicz-Łada, Ph.D.
Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland 
Katarzyna Kosicka-Noworzyń, PhD
Associate Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland- PS
Paulina Skupin-Mrugalska, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - MC
Mikolaj Czajkowski, MS
Ph.D. student
Poznan Univeristy of Medical Sciences
Poznan, Wielkopolskie, Poland - KK
Karolina Kustrzyńska, MS
Ph.D. student
Poznan Univeristy of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - AS
Aleksandra Szczepankiewicz, Ph.D.
Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - JN
Joanna Nowakowska-Lewicka, MS
Ph.D. student
Poznan Univeristy of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - BN
Beata Narożna, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Poznan Univeristy of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - WL
Wojciech Langwiński, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland - MR
Michał Romański, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Poznan University of Medical Sciences
Poznań, Wielkopolskie, Poland
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: The oligonucleotides were provided by ThermoFisher Scientific and were modified to increase their stability. The approximate masses for the unmodified oligonucleotides were 14 kDa for double-stranded mimics (miRNA 1 and miRNA 2) and 7 kDa for a single-stranded inhibitor (miRNA 3). The exact masses and modifications of the macromolecules were unknown due to the vendor’s policy. The LC-MS/MS analyses were carried out on an ExionLC system coupled to QTRAP 6500+ mass spectrometer (Sciex), in an electrospray negative ion mode (ESI-). Due to the well-known bad reputation of ion-pairing agents, both ion-pairing and non-ion-pairing conditions were investigated, and signal intensity was compared in the full scan mode (500 – 2000 m/z). We tested aqueous mobile phases with ammonium formate (AmmF), ammonium acetate (AmmA), ammonium bicarbonate (AmmB), triethylamine (TEA), and dimethylbutylamine (DMBA), the last two in combination with 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP). After mobile phase selection, the most intense precursor ions have been identified and their product ions screened. The chromatographic separation has been optimized with the use of bioZen Peptide XB-C18 column (Phenomenex). The LC-UV analyses were performed on the Agilent 1200 system at the wavelength of 260 nm. Three different columns (bioZen Oligo and bioZen Peptide PS-C18 from Phenomenex, and Nucleodur C18 Pyramid from Macherey-Nagel), two organic modifiers (methanol [MeOH] and acetonitrile [MeCN]), and two ion-pairing systems (TEA/HFIP and TEA/acetic acid [TEAA]) were tested.
Results: We encountered multiple challenges during method development, as listed in Table 1. Firstly, analyte resolution required high column temperature, at least 60 °C. Under those conditions, double-stranded miRNA mimics denatured and eluted as two separated strands. At lower temperatures, we observed two borderline scenarios: elution of all analytes with the mobile phase front (for a higher content of MeOH or MeCN in the mobile phase), or strong retention in the column without peak resolution (for a lower content). The other major findings included high susceptibility of chromatographic resolution and MS/MS detection to mobile phase composition, adsorption of miRNAs to the LC system, and failure of oligonucleotide-dedicated LC columns. Also, unknown molecular masses of the modified miRNAs initially impeded the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) optimization. We estimated these masses from the distribution of multi-charged precursor ions in the full scan mass spectra. Unfortunately, non-ion-pairing conditions (more instrument-friendly) showed poor ionization in LC-MS/MS for all tested microRNAs and could not be utilized, even though successfully used by other authors for various oligonucleotides [4].
Conclusion: LC-MS/MS and LC-UV techniques for miRNA analysis require careful optimization, including mobile phase composition, stationary phase, and column temperature. In the LC-UV method, the best results of miRNA separation were obtained under ion-pairing conditions using 100 mM TEAA, MeCN, and a polar-endcapped C18 column. In LC-MS/MS, the mobile phase composed of 5 mM DMBA, 100 mM HFIP, and MeOH was selected due to best sensitivity. The use of this phase, together with the bioZen Peptide column, enabled complete separation and sensitive detection of the studied miRNAs.
References: 1. O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C. Overview of microRNA biogenesis mechanism of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol. 2018;9:402.
2. Mestry C, Ashavaid TF, Swarup AS. Key methodological challenges in detecting circulating miRNAs in different biofluids. Ann Clin Biochem. 2023;60:14-26.
3. Liu A, Cheng M, Zhou Y, Deng P. Bioanalysis of oligonucleotide by LC-MS: effect of ion-pairing reagents and recent advances in ion-pairing free analytical strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15474.
4. Studzińska S, Bocian S, Rivoira L, Faden E, Faden G. Separation and identification of oligonucleotides impurities and degradation products by reversed phase ultra-high performance liquid chromatography using phenyl-bonded stationary phases without ion pairs - A step towards sustainability. J Chromatogr A. 2024;1736:465380.
Acknowledgements: This study received funding from the Polish Medical Research Agency (Agencja Badań Medycznych, grant No. 2024/ABM/03/KPO/KPOD.07.07-IW.07-0117/24-00). The authors declare no competing interest.
.jpg)
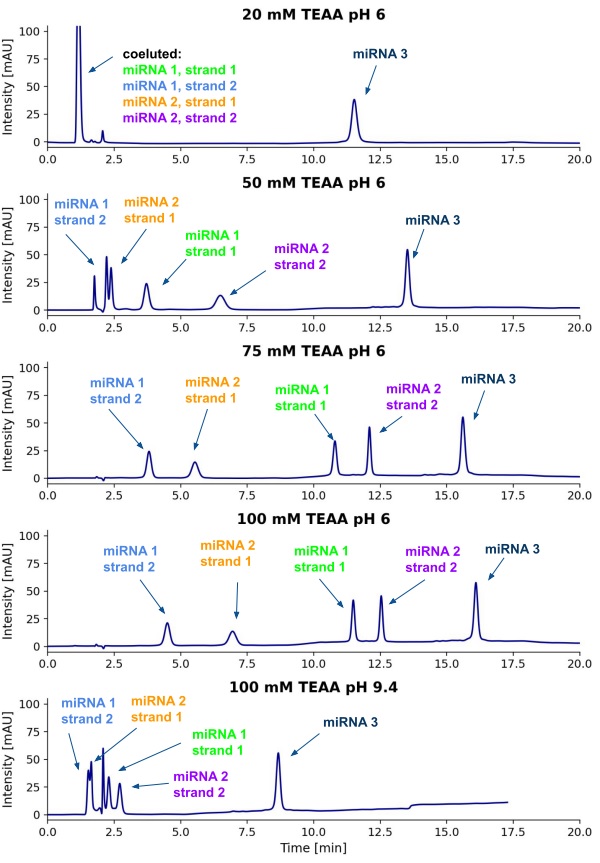 Figure 1. LC-UV chromatograms showing the influence of TEA concentration in the TEAA/MeCN mobile phase and/or pH (measured in mobile phase A) on the chromatographic resolution of miRNAs on Nucleodur C18 Pyramid column (5 µm, 150 x 4.6 mm). Aqueous solution of microRNAs with a concentration of 3 µM each was injected (injection volume - 10 µL). The optimal conditions, chosen for further works, included: column temperature - 60 °C, aqueous 100 mM TEAA solution pH 6 (mobile phase A) and 100 mM TEAA in 90% MeCN (mobile phase B), flow rate 1 mL/min with a gradient elution (0 - 6 min, 11% B; 6 - 15 min, 11 - 20% B; 15 - 18 min, 20% B; 18 - 19 min, 20 - 11% B; 19 - 24 min, 11% B).
Figure 1. LC-UV chromatograms showing the influence of TEA concentration in the TEAA/MeCN mobile phase and/or pH (measured in mobile phase A) on the chromatographic resolution of miRNAs on Nucleodur C18 Pyramid column (5 µm, 150 x 4.6 mm). Aqueous solution of microRNAs with a concentration of 3 µM each was injected (injection volume - 10 µL). The optimal conditions, chosen for further works, included: column temperature - 60 °C, aqueous 100 mM TEAA solution pH 6 (mobile phase A) and 100 mM TEAA in 90% MeCN (mobile phase B), flow rate 1 mL/min with a gradient elution (0 - 6 min, 11% B; 6 - 15 min, 11 - 20% B; 15 - 18 min, 20% B; 18 - 19 min, 20 - 11% B; 19 - 24 min, 11% B).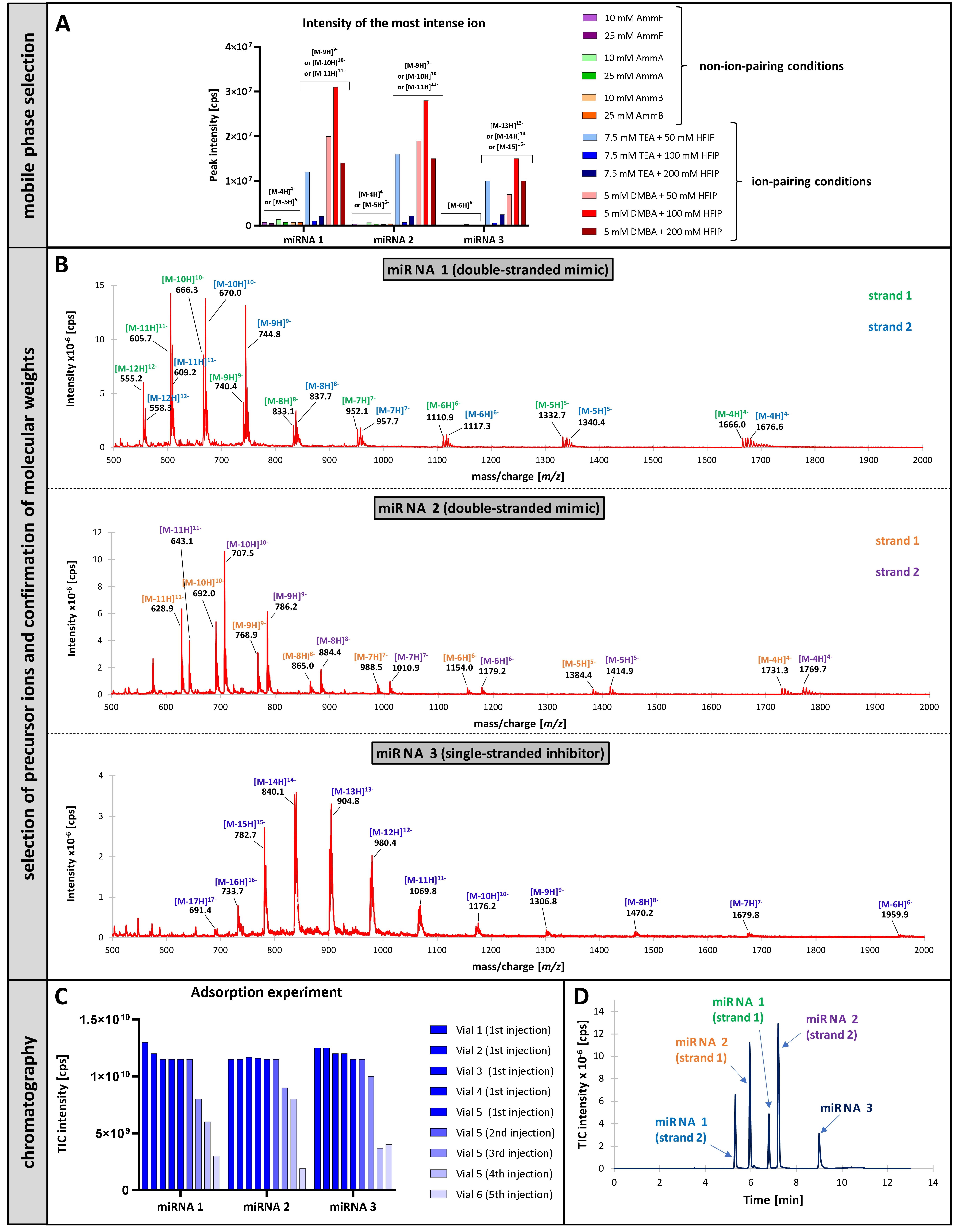 Figure 2. Results of the LC-MS/MS experiments: A) Impact of mobile phase composition on peak intensities and formation of ions with different charge states. B) Full scan modes for the selected mobile phase, 5 mM DMBA and 100 mM HFIP in water. C) Experiment investigating adsorption of miRNAs to autosampler needle. Experiments in panes A, B, and C were run in the full scan mode, under isocratic conditions with 20% MeOH. D) Chromatographic separation on a bioZen Peptide XB-C18 column (2.6 µm, 100 x 2.1 mm; mobile phase A – 5 mM DMBA and 100 mM HFIP in water, mobile phase B – MeOH; flow rate – 0.3 mL/min; gradient profile: 0 – 2 min, 12% B; 2 – 7.5 min, 12 – 18% B; 7.5 – 9.5 min, 18 – 95% B; 9.5 – 10.5 min, 95% B; 10.5 – 11 min, 95 – 12% B; 11 – 13.5 min, 12% B; column temperature – 75 °C; injection volume – 10 µL; injected sample – aqueous solution containing miRNA 1, 2, and 3 at a concentration of 0.1 µM each; experiment was run in the MRM mode with the most intense ions selected during optimization).
Figure 2. Results of the LC-MS/MS experiments: A) Impact of mobile phase composition on peak intensities and formation of ions with different charge states. B) Full scan modes for the selected mobile phase, 5 mM DMBA and 100 mM HFIP in water. C) Experiment investigating adsorption of miRNAs to autosampler needle. Experiments in panes A, B, and C were run in the full scan mode, under isocratic conditions with 20% MeOH. D) Chromatographic separation on a bioZen Peptide XB-C18 column (2.6 µm, 100 x 2.1 mm; mobile phase A – 5 mM DMBA and 100 mM HFIP in water, mobile phase B – MeOH; flow rate – 0.3 mL/min; gradient profile: 0 – 2 min, 12% B; 2 – 7.5 min, 12 – 18% B; 7.5 – 9.5 min, 18 – 95% B; 9.5 – 10.5 min, 95% B; 10.5 – 11 min, 95 – 12% B; 11 – 13.5 min, 12% B; column temperature – 75 °C; injection volume – 10 µL; injected sample – aqueous solution containing miRNA 1, 2, and 3 at a concentration of 0.1 µM each; experiment was run in the MRM mode with the most intense ions selected during optimization).