Bioanalytics - Biomolecular
(T0930-01-03) Investigating How Ionizable Lipids Impact the Cargo RNA Organization in Lipid Nanoparticles Using Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS)
Tuesday, November 11, 2025
9:30 AM - 10:30 AM CT
- VG
Viswanathan Gurumoorthy, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Research Associate
Merck & Co., Inc.
West Point, Pennsylvania, United States - VG
Viswanathan Gurumoorthy, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Research Associate
Merck & Co., Inc.
West Point, Pennsylvania, United States - MB
Marco A. Blanco, Ph.D.
Principal Scientist
Merck & Co., Inc.
West Point, Pennsylvania, United States - SP
Suzette Pabit, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Associate Principal Scientist
Merck & Co., Inc.
West Point, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are important delivery systems for therapeutic nucleic acids such as RNA [1]. Ionizable lipids, a key component of LNPs, gain a positive charge under acidic conditions, allowing them to form complexes with the negatively charged phosphate backbone of RNA. Attributes of RNA-LNPs, including particle size and shape, can significantly influence their in vivo performance [2,3], while process parameters such as the selection of lipids in formulations are used to modulate these attributes [4]. However, the composition of RNA-LNPs makes high-resolution structural determination challenging, raising questions regarding the overall shape and internal molecular arrangement of RNA-LNPs [5]. Therefore, there is a critical need for analytical tools capable of probing the shape and structural characteristics of RNA-LNPs. Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) is a solution-based technique that provides electron density distribution data for macromolecules and is widely employed to obtain shape information of biological macromolecules at nanometer resolution [6]. This study aims to explore the application of SAXS in the structural characterization of RNA-LNPs. Specifically, we seek to determine whether SAXS can elucidate differences in electron density distribution between empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs. To achieve this, we compare empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs formulated with different ionizable lipids to ascertain if the type of ionizable lipid influences the structural properties of RNA-LNPs.
Methods: Both empty and luciferase mRNA-loaded LNPs are similarly formulated except for the five different ionizable lipids used: proprietary lipid A, MC3, DODAP, ALC-0315, and SM-102. All these different LNP formulations are characterized by their particle size distribution and encapsulation efficiency. SAXS data for all LNPs are collected using a benchtop instrument with Cu Kα as an X-ray source. As depicted in Figure 1a, scattering intensities from LNPs filled into a quartz capillary are recorded on an area detector. The intensity from the detector is radially averaged to produce a SAXS profile I(q) vs. q (scattering vector in Å-1). SAXS data is collected over the q range: 0.003 – 1.5 Å-1. The size and shape information can be obtained from SAXS profiles at different q ranges as shown in Figure 1b. To analyze structural features observed in SAXS profiles, we use SasView [7] to employ the fitting function known as the broad peak model [8]. This allows for determining the Porod exponent, n, from the power law q-n and the peak position, q0, and correlation length, ξ, from the Lorentzian function. The Porod exponent from the model provides information about the shape of the particles, while the peak position corresponds to the correlation distance of the ordered arrangement in real space distance. The correlation length, inversely related to the peak width, indicates the distance after which the correlation of the positional order is lost [9].
Results: Representative SAXS profiles of both empty and mRNA-loaded are shown in Figure 2. At low q region, intensity of mRNA-loaded LNPs decays faster than empty LNPs (Fig.2), indicating that the particle size increases with mRNA loading comparable with the DLS results (Table 1). Similarly, from the intermediate q region, the Porod exponent is close to 4 (Table 1) indicating both empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs exhibit spherical features. Interestingly, all mRNA-loaded LNPs exhibit a peak between q = 0.07 – 0.1 Å-1. However, only empty LNPs with lipid A and MC3 show peaks, and their intensity is lower than that of mRNA-loaded LNPs. The peak around 0.1 Å-1 has been previously attributed to the ordered internal structure of RNA-LNPs [10,11]. The values from the model fitting are summarized in Table 1. Interestingly, the peak position and correlation lengths are similar between mRNA-loaded LNPs containing lipid A, MC3, and DODAP. Likewise, lipids with branched tails, ALC-0315 and SM-102, exhibit comparable peak properties despite variations in particle size and encapsulation efficiency. While the broad peak analysis helps in quantifying the peak features seen, ongoing work focuses on improving the SAXS analysis using physics-based models that can capture the electron density distribution between empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs.
Conclusion: SAXS profiles clearly show differences between empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs for all ionizable lipids. Also, a broad peak feature is consistently present in all mRNA-loaded LNPs. The peak positions and widths vary depending on the type of ionizable lipids used in the formulation. By employing a simplified analysis of SAXS data, we can effectively capture the differences between empty and loaded LNPs and classify the features based on lipid structures.
References: [1] Hou, X., et al. Nat Rev Mat 6.12 (2021): 1078-1094. [2] Eygeris, Y., et al. Acc Chem Res 55.1 (2021): 2-12. [3] Cheng, M. H. Y., et al. Adv Mat 35.31 (2023): 2303370. [4] Cárdenas, M, et al. Curr Opin in Colloid & Interface Sci 66 (2023): 101705. [5] Simonsen, J. B. J Control Release 373 (2024): 952-961. [6] Tokuda, JM., et al. Biophys Rev (2016): 139-149. [7] Doucet, M., et al. Zenodo. version 5.4 (2021). [8] Hammouda, B. National Institute of Standards and Technology 1 (2008). [9] Nele, V., et al. Langmuir 37.40 (2021): 11909-11921. [10] Yanez Arteta, M., et al. PNAS 115.15 (2018): E3351-E3360. [11] Gilbert, J., et al. J Colloid and Interface Sci 660 (2024): 66-76.
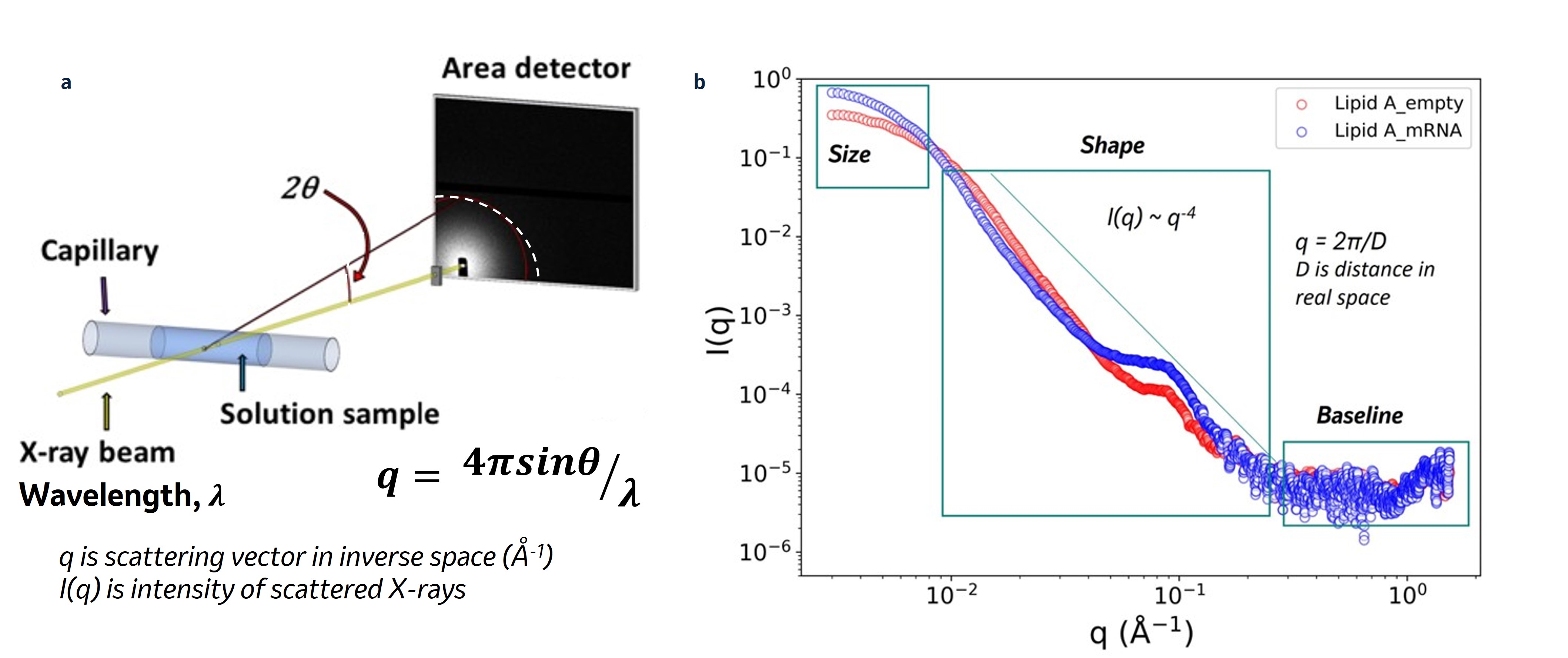 Figure 1. (a) SAXS experimental setup, adapted from [6], X-rays scattered from the sample in solution are collected in an area detector. The collected scattering intensity is radially integrated with respect to the main beam and reported as I(q) vs the scattering vector q (in Å-1) where q = (4π/)sin, is the X-ray wavelength and 2 the scattering angle. The SAXS profile, I(q) vs q, provides size and shape information about the sample. (b) SAXS profiles of empty and mRNA-loaded lipid A LNP normalized in terms of total lipid concentration. In the figure, we emphasized notable areas to look at to determine LNP size (at low q) and shape features (at mid q). The relationship q = 2π/D, where D is in real space, allows us to imagine the correlation of the scattering vector q to real space parameters.
Figure 1. (a) SAXS experimental setup, adapted from [6], X-rays scattered from the sample in solution are collected in an area detector. The collected scattering intensity is radially integrated with respect to the main beam and reported as I(q) vs the scattering vector q (in Å-1) where q = (4π/)sin, is the X-ray wavelength and 2 the scattering angle. The SAXS profile, I(q) vs q, provides size and shape information about the sample. (b) SAXS profiles of empty and mRNA-loaded lipid A LNP normalized in terms of total lipid concentration. In the figure, we emphasized notable areas to look at to determine LNP size (at low q) and shape features (at mid q). The relationship q = 2π/D, where D is in real space, allows us to imagine the correlation of the scattering vector q to real space parameters.
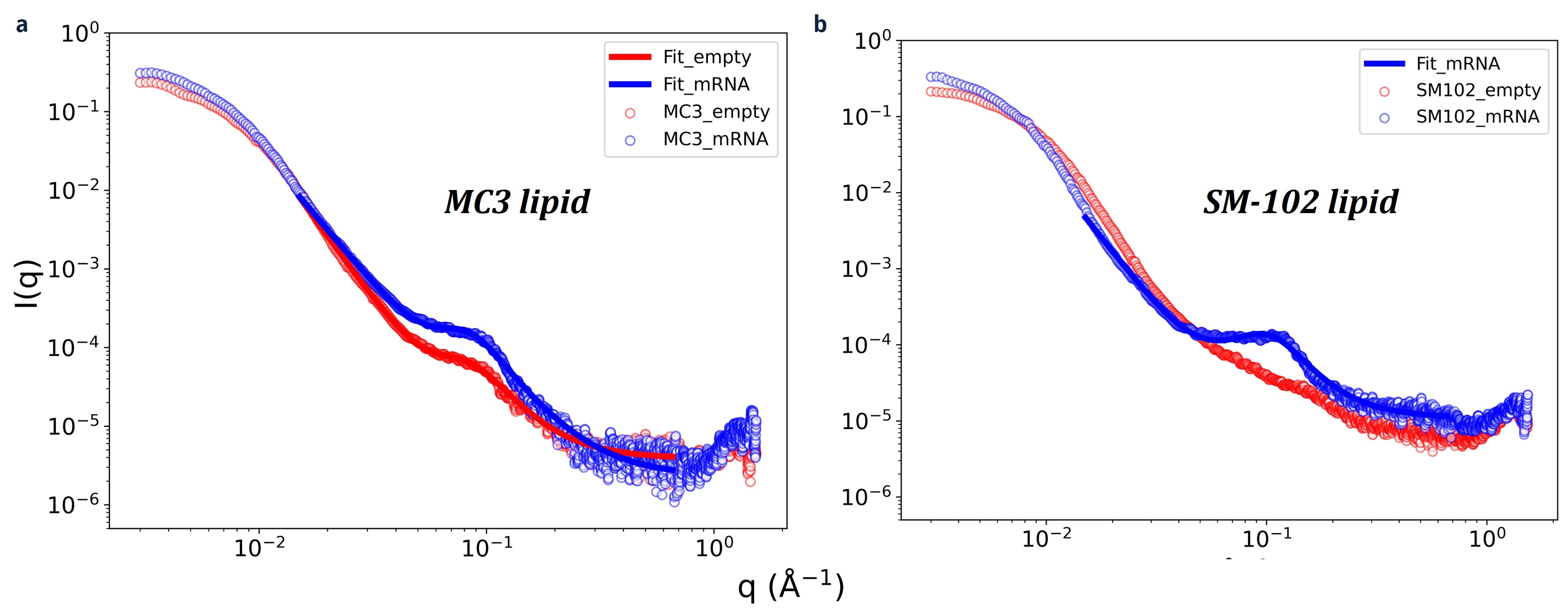 Figure 2. Representative SAXS profiles of (a) empty and mRNA-loaded MC3 LNPs and (b) empty and mRNA-loaded SM-102 LNPs. The solid lines represent the fits used to determine the Porod exponent, n, peak position, q0, and correlation length, ξ, as described in the Methods section. Note that for the empty LNP with SM-102, we did not fit the data as no peak can be observed.
Figure 2. Representative SAXS profiles of (a) empty and mRNA-loaded MC3 LNPs and (b) empty and mRNA-loaded SM-102 LNPs. The solid lines represent the fits used to determine the Porod exponent, n, peak position, q0, and correlation length, ξ, as described in the Methods section. Note that for the empty LNP with SM-102, we did not fit the data as no peak can be observed.
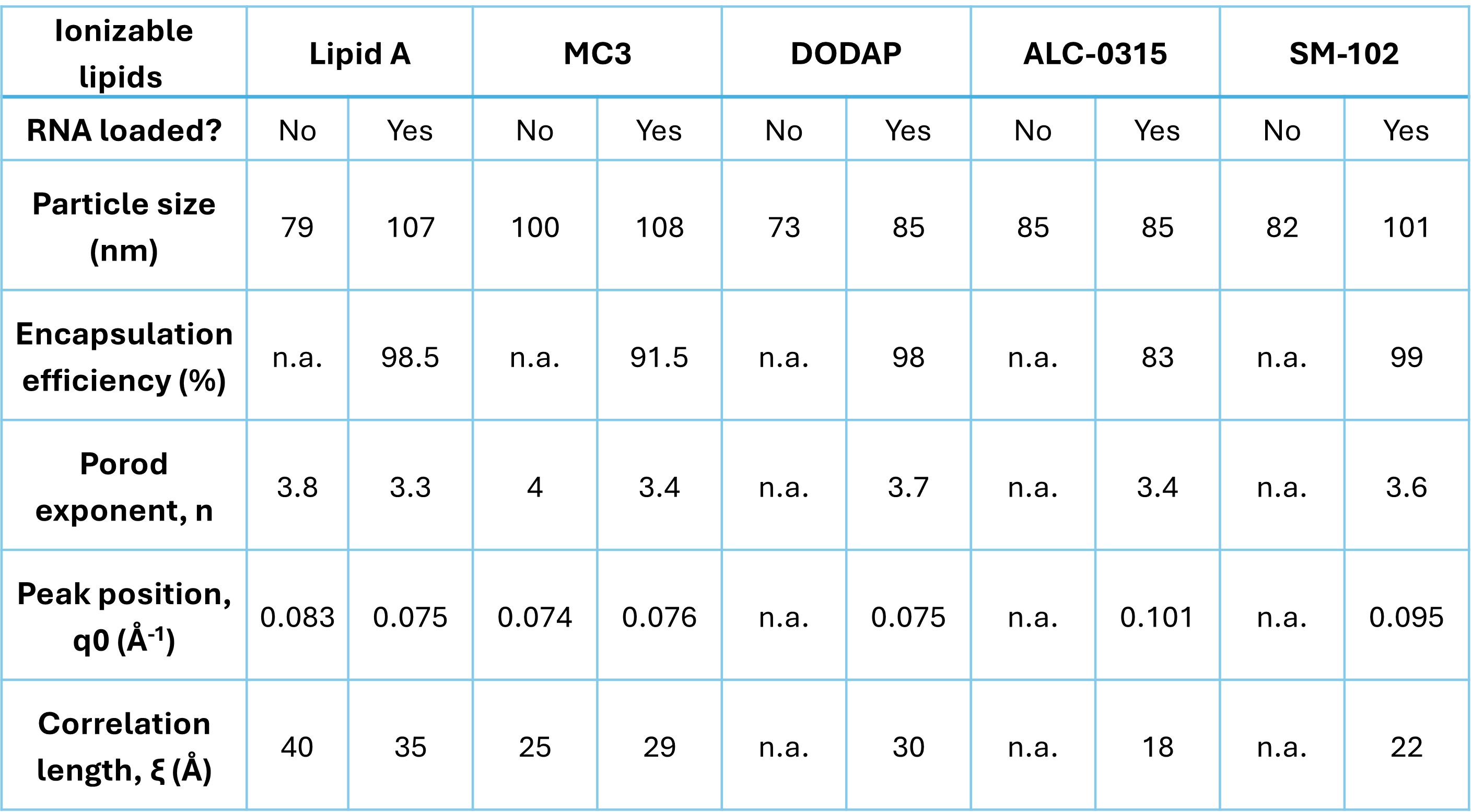 Table 1. Analytical measurements and results from the fitting as described in the Methods section. Encapsulation efficiency is not estimated for empty LNPs. Some empty LNPs do not exhibit a peak, and fitting is not performed. n.a. indicates not applicable or not calculated.
Table 1. Analytical measurements and results from the fitting as described in the Methods section. Encapsulation efficiency is not estimated for empty LNPs. Some empty LNPs do not exhibit a peak, and fitting is not performed. n.a. indicates not applicable or not calculated.
Methods: Both empty and luciferase mRNA-loaded LNPs are similarly formulated except for the five different ionizable lipids used: proprietary lipid A, MC3, DODAP, ALC-0315, and SM-102. All these different LNP formulations are characterized by their particle size distribution and encapsulation efficiency. SAXS data for all LNPs are collected using a benchtop instrument with Cu Kα as an X-ray source. As depicted in Figure 1a, scattering intensities from LNPs filled into a quartz capillary are recorded on an area detector. The intensity from the detector is radially averaged to produce a SAXS profile I(q) vs. q (scattering vector in Å-1). SAXS data is collected over the q range: 0.003 – 1.5 Å-1. The size and shape information can be obtained from SAXS profiles at different q ranges as shown in Figure 1b. To analyze structural features observed in SAXS profiles, we use SasView [7] to employ the fitting function known as the broad peak model [8]. This allows for determining the Porod exponent, n, from the power law q-n and the peak position, q0, and correlation length, ξ, from the Lorentzian function. The Porod exponent from the model provides information about the shape of the particles, while the peak position corresponds to the correlation distance of the ordered arrangement in real space distance. The correlation length, inversely related to the peak width, indicates the distance after which the correlation of the positional order is lost [9].
Results: Representative SAXS profiles of both empty and mRNA-loaded are shown in Figure 2. At low q region, intensity of mRNA-loaded LNPs decays faster than empty LNPs (Fig.2), indicating that the particle size increases with mRNA loading comparable with the DLS results (Table 1). Similarly, from the intermediate q region, the Porod exponent is close to 4 (Table 1) indicating both empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs exhibit spherical features. Interestingly, all mRNA-loaded LNPs exhibit a peak between q = 0.07 – 0.1 Å-1. However, only empty LNPs with lipid A and MC3 show peaks, and their intensity is lower than that of mRNA-loaded LNPs. The peak around 0.1 Å-1 has been previously attributed to the ordered internal structure of RNA-LNPs [10,11]. The values from the model fitting are summarized in Table 1. Interestingly, the peak position and correlation lengths are similar between mRNA-loaded LNPs containing lipid A, MC3, and DODAP. Likewise, lipids with branched tails, ALC-0315 and SM-102, exhibit comparable peak properties despite variations in particle size and encapsulation efficiency. While the broad peak analysis helps in quantifying the peak features seen, ongoing work focuses on improving the SAXS analysis using physics-based models that can capture the electron density distribution between empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs.
Conclusion: SAXS profiles clearly show differences between empty and mRNA-loaded LNPs for all ionizable lipids. Also, a broad peak feature is consistently present in all mRNA-loaded LNPs. The peak positions and widths vary depending on the type of ionizable lipids used in the formulation. By employing a simplified analysis of SAXS data, we can effectively capture the differences between empty and loaded LNPs and classify the features based on lipid structures.
References: [1] Hou, X., et al. Nat Rev Mat 6.12 (2021): 1078-1094. [2] Eygeris, Y., et al. Acc Chem Res 55.1 (2021): 2-12. [3] Cheng, M. H. Y., et al. Adv Mat 35.31 (2023): 2303370. [4] Cárdenas, M, et al. Curr Opin in Colloid & Interface Sci 66 (2023): 101705. [5] Simonsen, J. B. J Control Release 373 (2024): 952-961. [6] Tokuda, JM., et al. Biophys Rev (2016): 139-149. [7] Doucet, M., et al. Zenodo. version 5.4 (2021). [8] Hammouda, B. National Institute of Standards and Technology 1 (2008). [9] Nele, V., et al. Langmuir 37.40 (2021): 11909-11921. [10] Yanez Arteta, M., et al. PNAS 115.15 (2018): E3351-E3360. [11] Gilbert, J., et al. J Colloid and Interface Sci 660 (2024): 66-76.
 Figure 1. (a) SAXS experimental setup, adapted from [6], X-rays scattered from the sample in solution are collected in an area detector. The collected scattering intensity is radially integrated with respect to the main beam and reported as I(q) vs the scattering vector q (in Å-1) where q = (4π/)sin, is the X-ray wavelength and 2 the scattering angle. The SAXS profile, I(q) vs q, provides size and shape information about the sample. (b) SAXS profiles of empty and mRNA-loaded lipid A LNP normalized in terms of total lipid concentration. In the figure, we emphasized notable areas to look at to determine LNP size (at low q) and shape features (at mid q). The relationship q = 2π/D, where D is in real space, allows us to imagine the correlation of the scattering vector q to real space parameters.
Figure 1. (a) SAXS experimental setup, adapted from [6], X-rays scattered from the sample in solution are collected in an area detector. The collected scattering intensity is radially integrated with respect to the main beam and reported as I(q) vs the scattering vector q (in Å-1) where q = (4π/)sin, is the X-ray wavelength and 2 the scattering angle. The SAXS profile, I(q) vs q, provides size and shape information about the sample. (b) SAXS profiles of empty and mRNA-loaded lipid A LNP normalized in terms of total lipid concentration. In the figure, we emphasized notable areas to look at to determine LNP size (at low q) and shape features (at mid q). The relationship q = 2π/D, where D is in real space, allows us to imagine the correlation of the scattering vector q to real space parameters. Figure 2. Representative SAXS profiles of (a) empty and mRNA-loaded MC3 LNPs and (b) empty and mRNA-loaded SM-102 LNPs. The solid lines represent the fits used to determine the Porod exponent, n, peak position, q0, and correlation length, ξ, as described in the Methods section. Note that for the empty LNP with SM-102, we did not fit the data as no peak can be observed.
Figure 2. Representative SAXS profiles of (a) empty and mRNA-loaded MC3 LNPs and (b) empty and mRNA-loaded SM-102 LNPs. The solid lines represent the fits used to determine the Porod exponent, n, peak position, q0, and correlation length, ξ, as described in the Methods section. Note that for the empty LNP with SM-102, we did not fit the data as no peak can be observed. Table 1. Analytical measurements and results from the fitting as described in the Methods section. Encapsulation efficiency is not estimated for empty LNPs. Some empty LNPs do not exhibit a peak, and fitting is not performed. n.a. indicates not applicable or not calculated.
Table 1. Analytical measurements and results from the fitting as described in the Methods section. Encapsulation efficiency is not estimated for empty LNPs. Some empty LNPs do not exhibit a peak, and fitting is not performed. n.a. indicates not applicable or not calculated.