Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(T1430-09-59) Glyco-Conjugated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Enhance Meropenem Delivery against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Biofilms
- UN
Usha Y. Nayak, Ph.D.
Dr.
Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Manipal, Karnataka, India - AT
Ashwini T, M. Pharm
Dr.
Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences
UDUPI, Karnataka, India - HN
Hang T Nguyen, Ph.D.
Dr.
University of South Australia
Adelaide, South Australia, Australia - RC
Raghu Chandrashekar H, Ph.D.
Dr.
Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Udupi, Karnataka, India - YN
Yogendra Nayak, PhD (he/him/his)
Dr.
Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Udupi, Karnataka, India - PS
Padmaja A A. Shenoy, M.D.
Dr.
Kasturba Medical College
Udupi, Karnataka, India - AO
Abiodun D Ogunniyi, Ph.D.
Dr.
University of Adelaide
Adelaide, South Australia, Australia - SG
Sanjay Garg, Ph.D.
Professor
University of South Australia
Adelaide, South Australia, Australia
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: MSN were synthesized using modified Stöber method and functionalized with mannose (MN-MSN) and galactose (GL-MSN) via reductive amination. Meropenem (MP) loading was optimized using rotary evaporation method. Comprehensive characterization included FTIR, XRD, DSC, TGA, BET analysis, and electron microscopy. Antimicrobial efficacy was evaluated against clinical isolates of E. coli (n=23) and P. aeruginosa (n=24) using broth microdilution, time-kill kinetics, and biofilm assays. Safety of the formulation was assessed using haemolysis and cytotoxicity assays. Pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in Wistar rats following intravenous administration.
Results: Glyco-conjugated MSN demonstrated successful synthesis with particle sizes of 338.55±2.62 nm (MN-MSN) and 382.95±5.44 nm (GL-MSN). Drug loading achieved 692.95±5.03 mg/g (MP-MN-MSN) and 735.66±15.10 mg/g (MP-GL-MSN) with sustained release profiles following Korsmeyer-Peppas kinetics. Both formulations showed 8-fold enhanced antimicrobial potency compared to free meropenem: MIC₉₀ values of 0.004 μg/mL vs 0.031 μg/mL against E. coli, and 0.25 μg/mL vs 2 μg/mL against P. aeruginosa. Time-kill studies demonstrated complete bacterial eradication at concentrations 15-fold lower than the free drug. Anti-biofilm efficacy showed 73% biofilm mass reduction and 78% viability reduction against P. aeruginosa at 0.3-0.5 μg/mL. Excellent biocompatibility was observed with < 1.5% haemolysis and >95% cell viability. Pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated significant improvements: AUC increases of 2.5 to 3.4-fold for glycosylated MSNs versus free meropenem. Half-life extensions of 2.7 to 3.6-fold for glycosylated MSNs versus free drug (0.52 h) were achieved. The mean residence time extensions to 2.84 and 2.15 h (vs. 0.76 h) confirmed superior pharmacokinetic profiles.
Conclusion: Glyco-conjugated MSN successfully addressed clinical challenges of meropenem delivery through enhanced antimicrobial potency, superior biofilm penetration, and prolonged circulation time. The dual-targeting approach combining lectin-mediated bacterial recognition with sustained antibiotic release represents a paradigm shift in antimicrobial therapy. The 8-fold enhancement in potency with excellent safety profile supports clinical translation potential for treating biofilm-associated infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria.
References: 1. Sati H, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Hansen P, Garlasco J, Campagnaro E, et al. The WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List 2024: a prioritisation study to guide research, development, and public health strategies against antimicrobial resistance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2025;
2. Sharon N. Carbohydrates as future anti-adhesion drugs for infectious diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects. 2006 Apr;1760(4):527–37.
3. Narayan R, Gadag S, Cheruku SP, Raichur AM, Day CM, Garg S, et al. Chitosan-glucuronic acid conjugate coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A smart pH-responsive and receptor-targeted system for colorectal cancer therapy. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2021 Jun;261:117893.
4. Mukherjee MB, Mullick R, Reddy BU, et al. Galactose Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles As Delivery Vehicle in the Treatment of Hepatitis C Infection. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2020; 3: 7598–7610.
5. Mukhopadhyay, S. et al. Development of levofloxacin glycosylated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for urinary tract infections. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 2024 14:174–179.
6. Nguyen HT, Venter H, Veltman T, et al. In vitro synergistic activity of NCL195 in combination with colistin against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Int J Antimicrob Agents; 57. Epub ahead of print 1 May 2021. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106323.
Acknowledgements: The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, for providing facilities for the literature search. The authors also acknowledge and thank the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Government of India, New Delhi, for the fund support to Dr Usha Y Nayak (Ref. No. 35/13/2020-/Nano/BMS) and for granting Senior Research Fellowship to Ms Ashwini T. (Ref. No. AMR/Fellowship/25/2022- ECD-11). Would like to thank Lora Bowes, Thi Hoang, Judith Holds and Max McClafferty at the University of South Australia for their technical assistance. The authors acknowledge the instruments and scientific and technical assistance of Microscopy Australia at Adelaide Microscopy, The University of Adelaide, a facility that is funded by the university and state and federal governments.
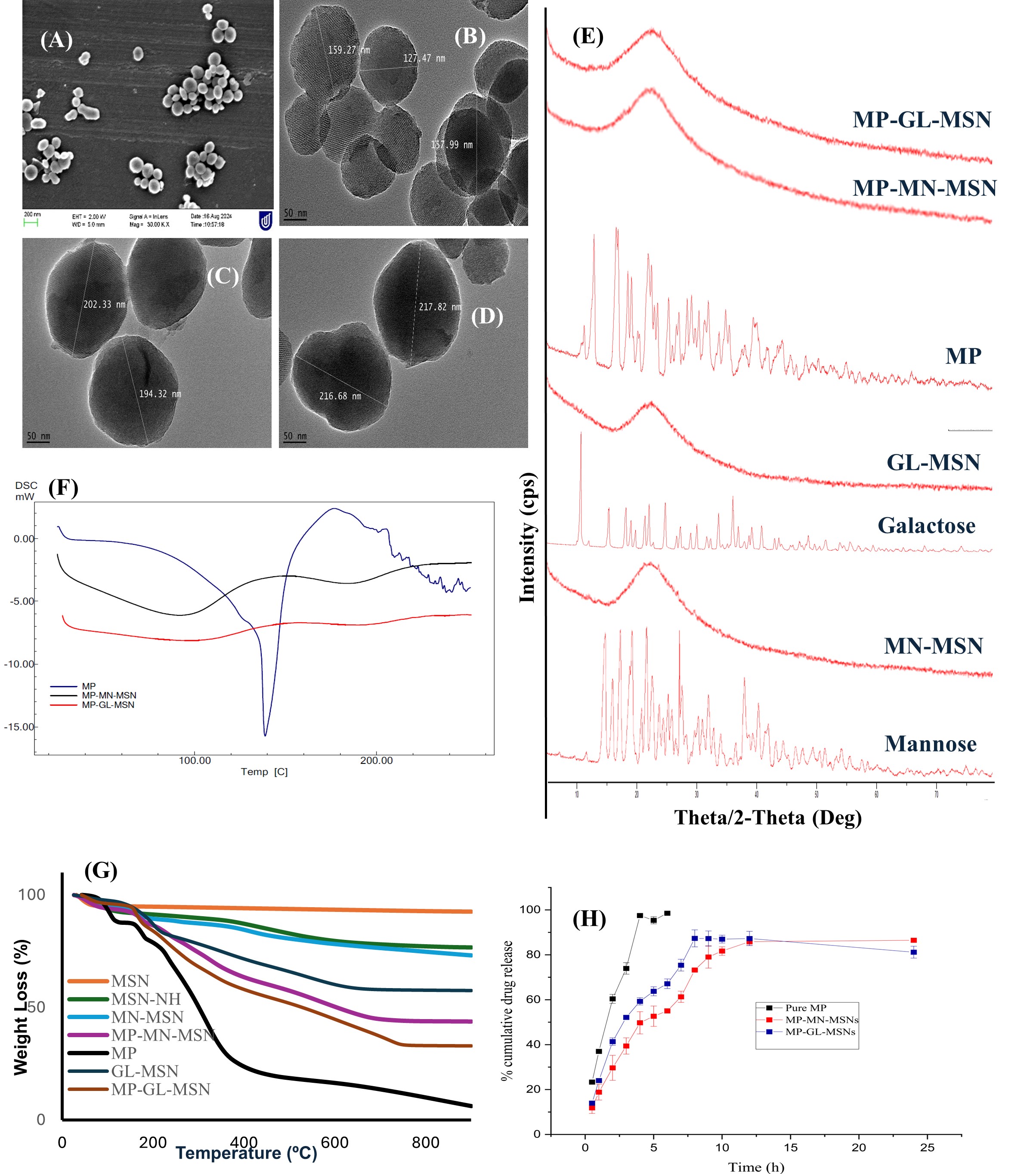 Fig.1. Characterization of MP loaded glyco-conjugated MSN. SEM images for (A) MSN-NH; TEM images for (B) GL-MSN (C) MP-MN-MSN (D) MP-GL-MSN; (E) XRD pattern for mannose, galactose, glyco-conjugated MSN, Pure MP, MP loaded Glyco-conjugated MSN; (F) DSC thermogram of Pure MP and MP loaded glyco-conjugated MSN; (G) TGA of MSN, amine functionalized MSN, glyco-conjugated MSN, Pure MP, MP loaded Glyco-conjugated MSN; (H) In vitro release profiles of meropenem from glyco-conjugated MSN.
Fig.1. Characterization of MP loaded glyco-conjugated MSN. SEM images for (A) MSN-NH; TEM images for (B) GL-MSN (C) MP-MN-MSN (D) MP-GL-MSN; (E) XRD pattern for mannose, galactose, glyco-conjugated MSN, Pure MP, MP loaded Glyco-conjugated MSN; (F) DSC thermogram of Pure MP and MP loaded glyco-conjugated MSN; (G) TGA of MSN, amine functionalized MSN, glyco-conjugated MSN, Pure MP, MP loaded Glyco-conjugated MSN; (H) In vitro release profiles of meropenem from glyco-conjugated MSN.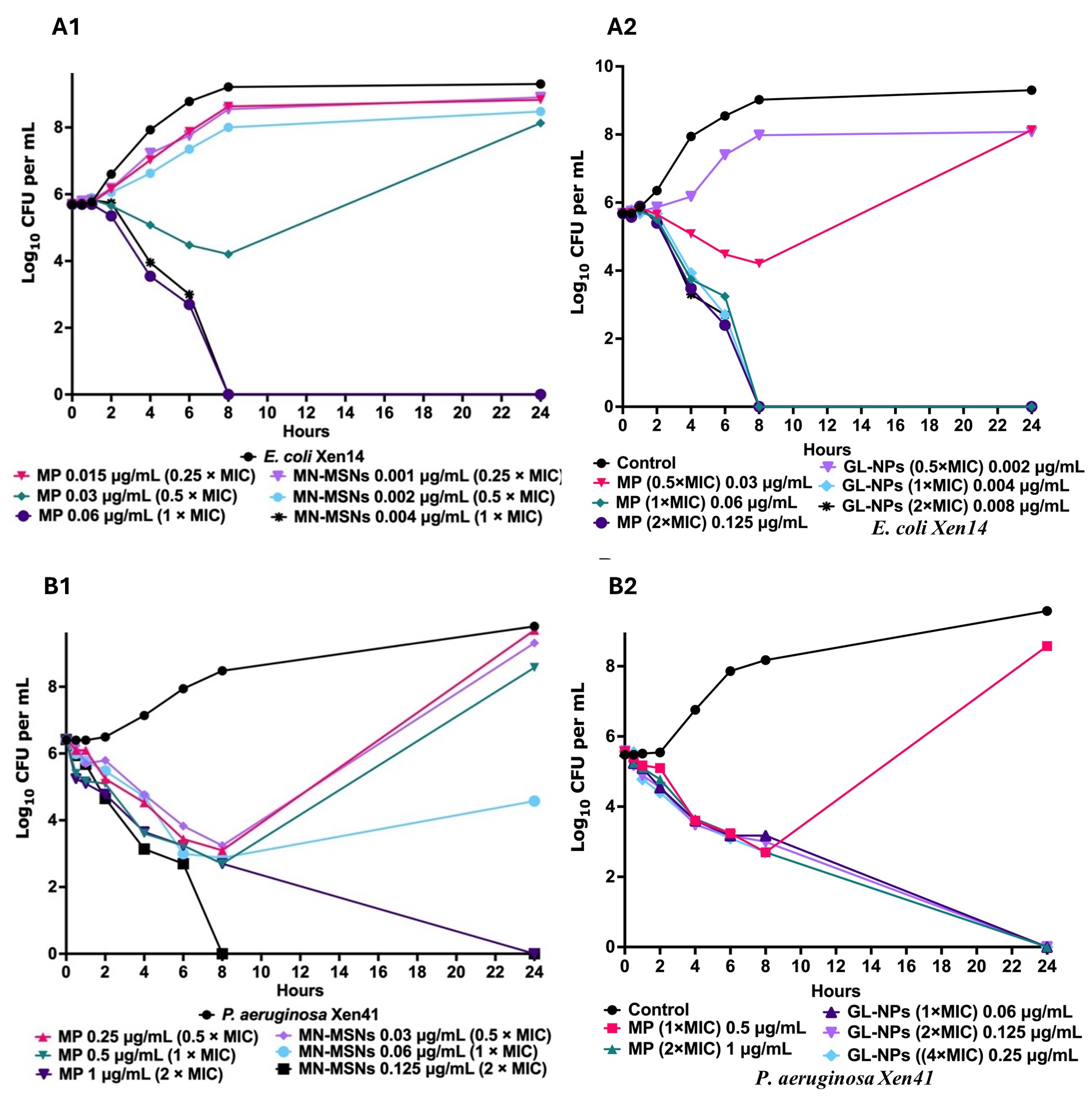 Fig. 2. Time- and concentration-killing and growth-inhibitory kinetics of MP, MP loaded MN-MSNs (MN-MSNs), and MP loaded GL-MSNs (GL-MSNs) against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. MP, MN-MSNs and GL-MSNs were prepared at various concentration of 0.25 MIC, 0.5 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC. (A1, A2, B1, and B2) time-killing kinetics of MP loaded MN-MSNs and MP loaded GL-MSNs in comparison with MP against tested bacteria; tests were prepared in duplicate in 24 well-flat bottom plates (CLS3738, Sigma-Aldrich), then samples were withdrawn at indicated times for serial dilutions and plating and incubation at 37°C overnight on HBA plates. MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.
Fig. 2. Time- and concentration-killing and growth-inhibitory kinetics of MP, MP loaded MN-MSNs (MN-MSNs), and MP loaded GL-MSNs (GL-MSNs) against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. MP, MN-MSNs and GL-MSNs were prepared at various concentration of 0.25 MIC, 0.5 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC. (A1, A2, B1, and B2) time-killing kinetics of MP loaded MN-MSNs and MP loaded GL-MSNs in comparison with MP against tested bacteria; tests were prepared in duplicate in 24 well-flat bottom plates (CLS3738, Sigma-Aldrich), then samples were withdrawn at indicated times for serial dilutions and plating and incubation at 37°C overnight on HBA plates. MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.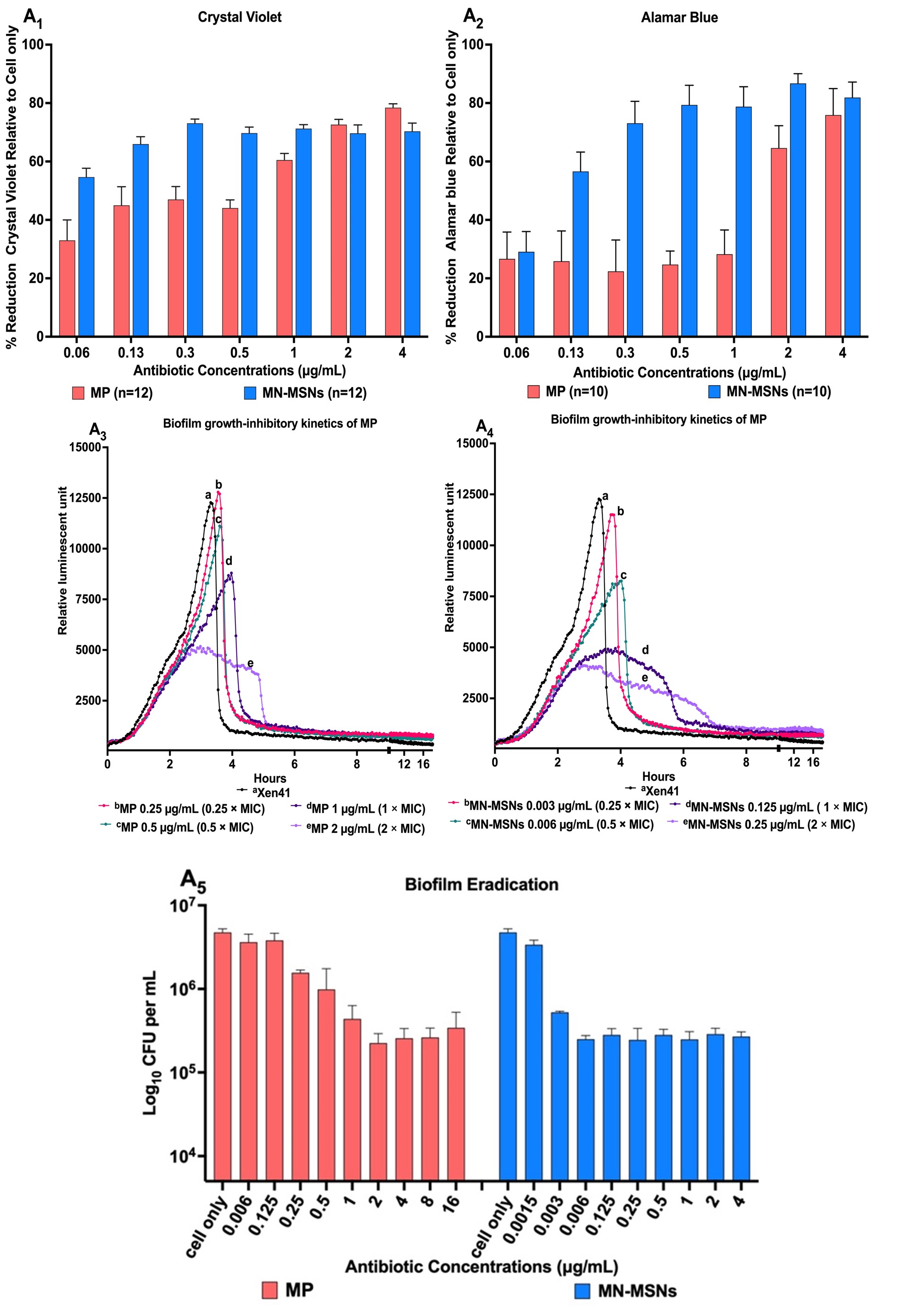 Fig.3. Comparison of anti-biofilm activities of MN-MSNs with MP against P. aeruginosa (Xen41). A mature biofilm of P. aeruginosa was generated by growth at 24 h in 96-well plates. (A1) presenting reduction in Xen41 biofilm mass following 24 h treatment with MP and MP-loaded MN-MSNs (MN-MSNs) was quantified using crystal violet staining. (A2) reduction in Xen41 viability in biofilm flowing 24 h treatment with MP and MN-MSNs, cell viability was quantified using Alamar Blue. (A3 & A4) showing time and concentration- Xen41 viability kinetics in biofilm measured by changes in bacterial metabolic activity relative to the reduction of Xen41 luminescence compared with growth control. (A5) presenting the total number of viable Xen41 cells remaining on pegs of MBEC lid after treatment with different concentrations of MN-MSNs and MP. Data represents mean standard deviation (n=12 [crystal violet]; n=10 [Alamar Blue]; n=4 [MBEC]).
Fig.3. Comparison of anti-biofilm activities of MN-MSNs with MP against P. aeruginosa (Xen41). A mature biofilm of P. aeruginosa was generated by growth at 24 h in 96-well plates. (A1) presenting reduction in Xen41 biofilm mass following 24 h treatment with MP and MP-loaded MN-MSNs (MN-MSNs) was quantified using crystal violet staining. (A2) reduction in Xen41 viability in biofilm flowing 24 h treatment with MP and MN-MSNs, cell viability was quantified using Alamar Blue. (A3 & A4) showing time and concentration- Xen41 viability kinetics in biofilm measured by changes in bacterial metabolic activity relative to the reduction of Xen41 luminescence compared with growth control. (A5) presenting the total number of viable Xen41 cells remaining on pegs of MBEC lid after treatment with different concentrations of MN-MSNs and MP. Data represents mean standard deviation (n=12 [crystal violet]; n=10 [Alamar Blue]; n=4 [MBEC]).