Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(W1130-08-50) Development of Long-Acting Injectable Formulations of Next Generation Diarylquinolines for Preventive Therapy of Tuberculosis Infection
.jpg)
James J. Hobson, PhD
Research Coordinator
University of Liverpool
LIVERPOOL, England, United Kingdom.jpg)
James J. Hobson, PhD
Research Coordinator
University of Liverpool
LIVERPOOL, England, United Kingdom- NA
Nicole Ammerman, Ph.D.
Research Associate
Johns Hopkins University
Baltimore, Maryland, United States - SL
Si-Yang Li, Ph.D.
Research Fellow
Johns Hopkins University
Baltimore, Maryland, United States - JM
Jonathan Massam, BS
Research Technician
University of Liverpool
Liverpool, England, United Kingdom - JS
Jo Sharp, Ph.D.
Programme Manager
University of Liverpool
Liverpool, England, United Kingdom - EN
Eric Nuermberger, M.D.
Professor of Medicine and International Health
Johns Hopkins University
Baltimore, Maryland, United States - AO
Andrew Owen, Ph.D.
Professor of Pharmacology
University of Liverpool
Liverpool, England, United Kingdom - SR
Steve P. Rannard
Professor of Chemistry
University of Liverpool
Liverpool, England, United Kingdom
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: To develop LAIs of TBAJ-876, high throughput precipitation freeze dry screening was conducted using combinations of excipients that are listed on the FDA’s CDER inactive ingredients database. TBAJ-876 was dissolved in 50:50 acetone/methanol and added to excipients dissolved in water, inducing rapid precipitation. These suspensions were frozen in liquid nitrogen and freeze dried to produce a powder consisting of particles of TBAJ-876 stabilised by excipients. The lead formulations identified from freeze dry screening were transferred to a precipitation spray drying method to increase scale and aid clinical translation. Precipitation was induced under constant stirring and followed by sonication. Suspensions were spray dried using a Buchi B-290 to produce a final dry powder for reconstitution.
Results: Screening conducted at API loadings between 50-80 wt% with respect to total dry powder mass, yielded a total of 529 combinations. Following assessment of physical characteristics, 68 of these were taken forward for lead optimisation. Formulations were iteratively optimised and a total of 3 lead formulations containing up to 80 wt% of TBAJ-876 were selected for preclinical evaluation of pharmacokinetic profile and efficacy in a validated BALB/c mouse model of TB preventative therapy. Particle size was confirmed via dynamic light scattering (figure 1) and crystalline characteristics were observed via powder x-ray diffraction and Scanning Electron Microscopy analysis (figure 2). Maximum syringeability of lead formulations was 400 mg of TBAJ-876 + 1 mL of water. Formulations were administered intramuscularly in vivo in a paucibacillary mouse model of TPT, with lung Mycobacterium tuberculosis colony-forming unit counts and plasma TBAJ-876 exposures measured. All formulations had bactericidal activity that was superior to oral BDQ at a human-equivalent dose and similar to the same total TBAJ-876 dose given orally over 4 weeks (figure 3), providing proof-of-concept for a highly efficacious LAI regimen for TPT.
Conclusion: The data suggests that these formulations of TBAJ-876 could be used for a highly efficacious single dose TPT regimen administered as an intramuscular LAI. Further preclinical assessment is now warranted, including human dose prediction and safety and tolerability studies.
Acknowledgements: The work presented was funded by NIH-NIAID grant R61-AI-161809
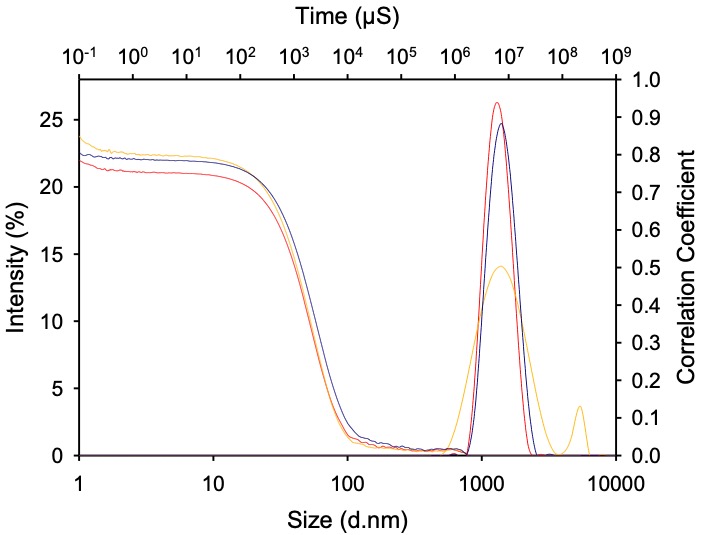 Figure 1. Representative particle size distribution of formulation lead at 50 wt% (red), 70 wt% (yellow) and 80 wt% (blue) TBAJ-876 relative to excipient stabiliser. Hydrodynamic diameters of particles ranged from 1640 to 1880 nm, determined via dynamic light scattering using a Malvern Panalytical ZetaSizer Ultra
Figure 1. Representative particle size distribution of formulation lead at 50 wt% (red), 70 wt% (yellow) and 80 wt% (blue) TBAJ-876 relative to excipient stabiliser. Hydrodynamic diameters of particles ranged from 1640 to 1880 nm, determined via dynamic light scattering using a Malvern Panalytical ZetaSizer Ultra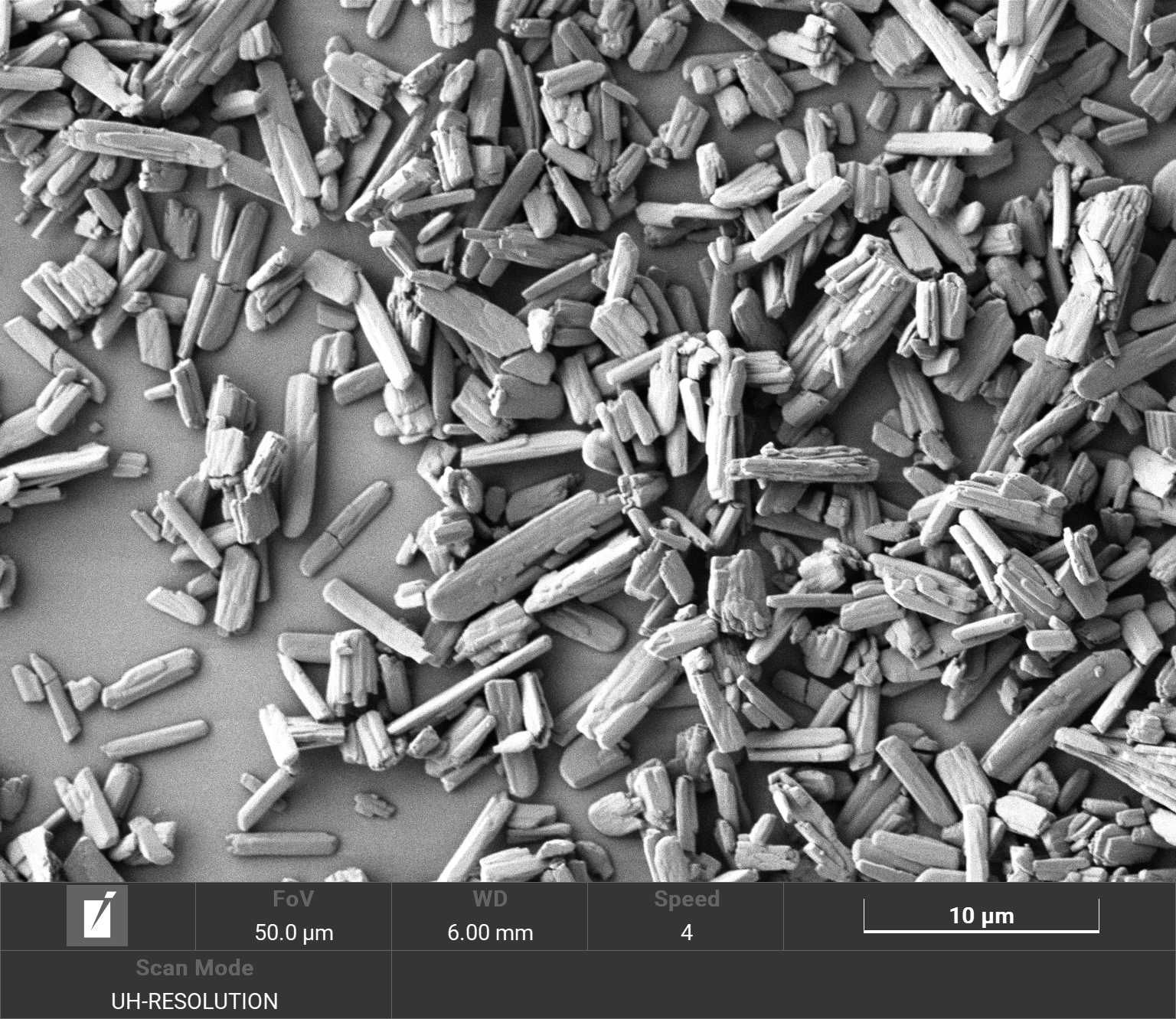 Figure 2. Scanning electron micrograph of a representative lead formulation with 80 wt% loading TBAJ-876.
Figure 2. Scanning electron micrograph of a representative lead formulation with 80 wt% loading TBAJ-876.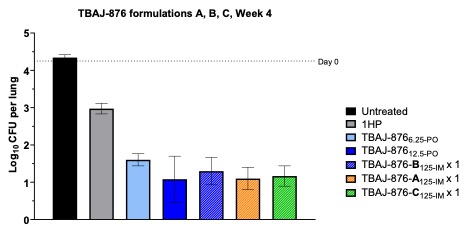 Figure 3. Bactericidal activity of TBAJ-876 lead formulations (TBAJ-876-A, B, C) after IM injection in a BALB/c mouse model of TB preventative therapy. Data compared with untreated control, oral isoniazid-rifapentine (1HP) and oral TBAJ-876 (TBAJ-876-PO).
Figure 3. Bactericidal activity of TBAJ-876 lead formulations (TBAJ-876-A, B, C) after IM injection in a BALB/c mouse model of TB preventative therapy. Data compared with untreated control, oral isoniazid-rifapentine (1HP) and oral TBAJ-876 (TBAJ-876-PO).