Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(M0930-08-50) Engineering Stimuli-Responsive Hierarchical Nanogels for Programmable Pulsatile Oral Vaccine Delivery
- ID
Ishaan Duggal, MS
PhD Student
University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States - ID
Ishaan Duggal, MS
PhD Student
University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States - RS
Rohini Sreenivasan
Undergraduate Assistant
University of Texas at Austin
AUSTIN, Texas, United States - RP
Ridhi Patil, BS
Undergraduate Assistant
University of Texas at Austin
AUSTIN, Texas, United States - BM
Brinkley Morse, BS
Undergraduate Assistant
University of Texas at Austin
AUSTIN, Texas, United States - AA
Ananya Anand
Undergraduate Assistant
University of Texas at Austin
AUSTIN, Texas, United States - AV
Armaan Verma
Undergraduate Assistant
University of Texas at Austin
AUSTIN, Texas, United States - NP
Nicholas A. Peppas, Ph.D.
Professor
University of Texas at Austin
AUSTIN, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: The delivery platform is based on hierarchical nanoparticles synthesized from Poly (acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) copolymers synthesized via inverse emulsion polymerization. Systematic variation of comonomer ratios, surfactant/co-surfactant concentrations, and crosslinker type and content enabled precise control over polymer composition, particle size, crosslinking density, and degradation kinetics. Molecular imprinting strategies were employed to assess whether selective antigen recognition by imprinted nanogels modulates the resulting immune response. Hierarchical assembly was achieved through electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition of polyethylenimine (PEI) and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides to enhance mucosal uptake and activate antigen-presenting cells. At the core, antigen-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles encapsulating ovalbumin (OVA) as a model antigen are being used to achieve a delayed secondary release pulse designed to mimic booster-like kinetics. Physicochemical characterization included dynamic light scattering for pH-responsive size and polydispersity, electron microscopy for morphology, titrimetric analysis for acidic group density, microBCA assays for protein loading and release efficiency, and spectroscopic methods to confirm chemical composition. In vitro release studies under simulated gastrointestinal pH conditions validated pulsatile behavior, while cytotoxicity was assessed using MTS and LDH assays. Future work will focus on comprehensive in vivo immunogenicity studies to evaluate the platform’s efficacy. Systemic immune responses will be quantified by measuring serum IgG titers using ELISA, while mucosal immunity will be assessed via secretory IgA levels in feces, saliva, or intestinal washes. Cellular immunity will be evaluated through T-cell proliferation assays and cytokine profiling using ELISpot and flow cytometry. These studies aim to confirm that the platform elicits both mucosal and systemic immune responses following a single oral dose, mimicking the kinetics of primary and secondary immune responses and supporting the long-term protective potential of pulsatile antigen delivery. These findings establish a versatile nanogel design framework for pulsatile oral vaccine delivery with potential to enhance compliance and eliminate booster dosing.
Results: Poly (acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) nanogels showed clear pH-responsive behavior wherein a sharp size reduction from around 220 nm at pH 7 to around 60 nm at pH 3 could be observed indicating network collapse in acidic conditions. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed spherical particles with uniform distribution. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed characteristic peaks for ester carbonyl (~1730 cm⁻¹) and carboxylate groups (~1550 cm⁻¹), confirming successful incorporation of itaconic acid, acrylamide, and the crosslinker. Varying the itaconic acid content influenced both the swelling behavior and protein loading capacity. Potentiometric titration confirmed increasing carboxylic acid content with higher IA feed ratios, and microBCA assays showed that ovalbumin (OVA) loading efficiencies exceeded 90%. In vitro release tests showed full release of the loaded protein within 24 hours under simulated intestinal conditions. Currently the loading and release studies with the PLGA core loaded nanoparticles are being performed to achieve the delayed secondary release. Layer-by-layer coating with polyethylenimine (PEI) and CpG oligonucleotides didn’t affect particle structure, as confirmed by DLS and TEM. This electrostatic layering is expected to enhance uptake through mucosal surfaces and improve immune activation by boosting interactions with intestinal epithelial and immune cells. Biocompatibility was assessed using MTS and LDH assays in intestinal epithelial and immune cell lines, with cell viability remaining above 90% and minimal signs of membrane damage. Overall, the nanogels remained stable, non-toxic, and well-suited for oral delivery.
Conclusion: This study successfully demonstrates the design and characterization of a programmable, stimuli-responsive oral vaccine delivery system capable of achieving pulsatile antigen release that mimics natural immune activation patterns. The hierarchical nanogel platform combines pH-sensitive swelling, degradable crosslinkers, and molecular imprinting to finely tune release kinetics and antigen loading. The electrostatic layering of PEI and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides enhances mucosal uptake and immune stimulation, while encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles provide a sustained secondary release pulse to prolong immune activation. Ongoing work focuses on in vivo immunogenicity studies and further optimization of nanoparticle composition to tailor release kinetics for various vaccine targets.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the Cockrell Family Chair Foundation, the Office of the Dean of the Cockrell School of Engineering at the University of Texas at Austin (UT) for the Institute for Biomaterials, Drug Delivery, and Regenerative Medicine, and the UT-Portugal Collaborative Research Program.
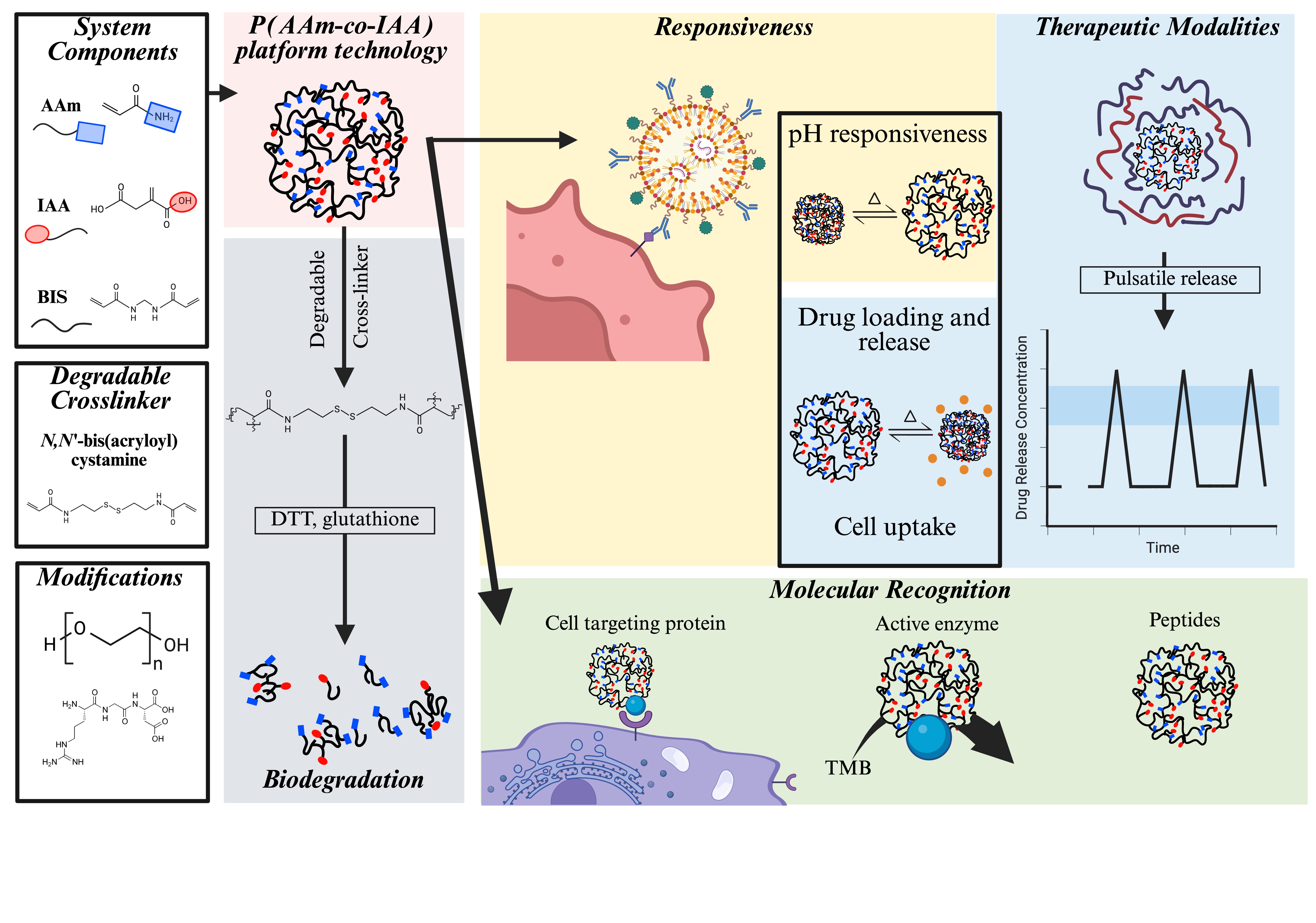 Schematic overview of the hierarchical nanoparticle-based oral vaccine delivery platform designed for programmable, pulsatile antigen release.
Schematic overview of the hierarchical nanoparticle-based oral vaccine delivery platform designed for programmable, pulsatile antigen release.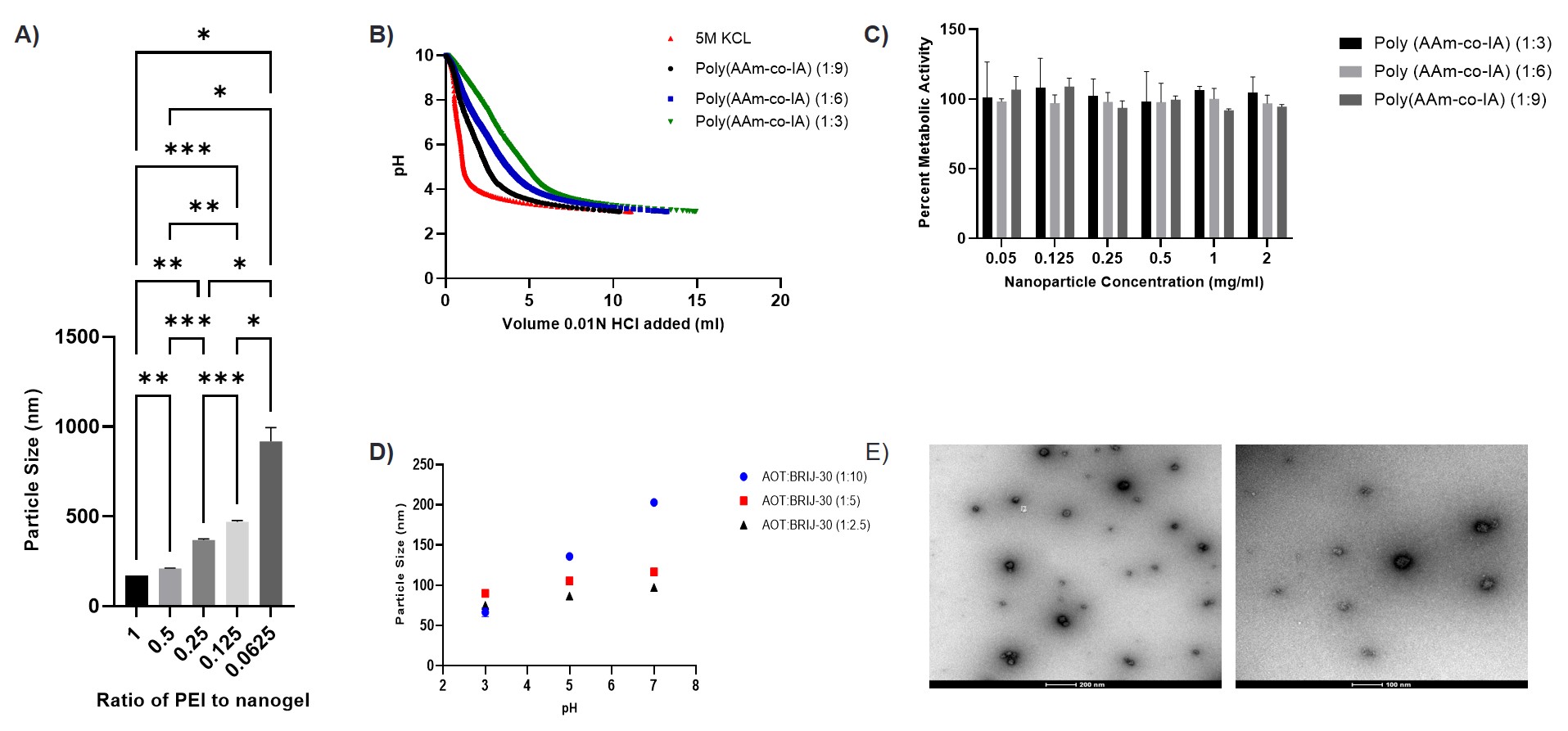 Figure 2 (A) Particle size increases with PEI:nanogel ratio, indicating successful layer-by-layer deposition of polycationic PEI. (B) Titrimetric analysis of carboxylic acid content shows variable HCl consumption across formulations with differing itaconic acid and acrylamide composition. (C) MTS assay confirms >90% cell viability across formulations, indicating high in vitro biocompatibility. (D) DLS measurements illustrate changes in hydrodynamic diameter with varying surfactant/co-surfactant ratios, confirming size tunability during synthesis. (E) Transmission electron microscopy reveals spherical nanogels (scale bar =200 and 100 nm).
Figure 2 (A) Particle size increases with PEI:nanogel ratio, indicating successful layer-by-layer deposition of polycationic PEI. (B) Titrimetric analysis of carboxylic acid content shows variable HCl consumption across formulations with differing itaconic acid and acrylamide composition. (C) MTS assay confirms >90% cell viability across formulations, indicating high in vitro biocompatibility. (D) DLS measurements illustrate changes in hydrodynamic diameter with varying surfactant/co-surfactant ratios, confirming size tunability during synthesis. (E) Transmission electron microscopy reveals spherical nanogels (scale bar =200 and 100 nm).