Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(T1130-08-52) Identification of Formulation Design Space for Quetiapine Fumarate Extended-Release Tablets across Strengths

Zekun Li, MS (he/him/his)
PhD Student
Northeastern University
Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Zekun Li, MS (he/him/his)
PhD Student
Northeastern University
Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Weizhou Yue, Ph.D.
Postdoc
Northeastern University
Boston, Massachusetts, United States- MJ
Megan Johnsen, BS
Undergraduate student
Northeastern University
Boston, Massachusetts, United States - DS
Daniel M. Shen
Student
Northeastern University
Boston, Massachusetts, United States - SA
Saleh Allababidi, Ph.D.
Associate Teaching Professor
University of Rhode Island
Kingston, Rhode Island, United States - WS
Wei-Jhe Sun, Ph.D.
Senior Pharmacologist
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States 
Sami Nazzal, PhD (he/him/his)
Senior Pharmacologist
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States
Manar AI-Ghabeish, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Senior Pharmacologist
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States
Heather J. Boyce, Ph.D.
LEAD PHARMACOKINETICIST
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States.jpg)
Fang Wu, Ph.D.
Review Senior Pharmacologist
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States- ZZ
Zhen Zhang, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
Master Pharmacologist
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States - RD
Renishkumar R. Delvadia, Ph.D.
Senior CMC Drug Product Reviewer
US Food and Drug Administration
Silver Spring, Maryland, United States 
Jie Shen, Ph.D. (she/her/hers)
Professor
Northeastern University
Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: The marketed quetiapine fumarate (QF) ER matrix tablet, available in multiple strengths (e.g., EQ 200 mg Base and EQ 300 mg Base), Seroquel XR®, was chosen as the reference listed drug (RLD) product. Laboratory-made (LM) QF ER tablets produced at the same strengths as these of the RLD were prepared using wet granulation and tablet compression procedures. Quality-by-Design (QbD) principles were implemented to identify the impact of key formulation variables (e.g., HPMC amount (20%-40%, w/w) and ratio of different grades of HPMC (0.2-2)) and their potential interactions on in vitro QF release characteristics. Design of Experiment (DoE) studies (e.g., response surface model (RSM)) using JMP® by SAS were conducted separately for each strength. Critical quality attributes (e.g., content uniformity, dimension, and hardness) were systemically evaluated and compared to the respective RLD strength. In addition, in vitro dissolution testing of the QF tablet formulations were conducted at 37°C using USP apparatus I at 200 rpm (250 rpm after 24 hr) with 20 mesh baskets in biphasic media (0.05 M citric acid and 0.09 N NaOH, pH 4.8 for first 5 hours followed by the addition of 100 mL of 0.05 M dibasic sodium phosphate dodecahydrate and 0.46 N NaOH to achieve a final pH of 6.6) (n=3, mean±SD). Dissolution samples were withdrawn at pre-determined time points and analyzed using a validated high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. For the comparison of dissolution profiles, the similarity factor (f2) was calculated. The RLD products were studied as controls. Finally, statistical data analysis was conducted using JMP®.
Results: The LM QF tablet formulations across multiple strengths exhibited similar weight, dimensions, and hardness compared to their respective RLD products. The formulation variables (e.g., HPMC K100LV/K4M ratio) and their interactions (e.g., total HPMC*K100LV/K4M, K100LV/K4M2, total HPMC2) were identified as key parameters influencing f2 values of the LM QF formulations cross multiples strengths (p < 0.05). Following the DoE studies, response surface plots for the EQ 200 mg Base and EQ 300 mg Base strength were generated to define formulation design spaces within which the LM QF formulations showed similar dissolution profiles compared to the respective RLD product with a f2 value over 50 (Figure 1). It was also demonstrated that QF ER tablet formulations with dissimilar compositional proportionality exhibited similar in vitro QF dissolution profiles (Figure 2). Lastly, the in vitro QF dissolution profiles tested in two different biphasic media overlapped, indicating that the biphasic method recommended in the FDA dissolution database for QF ER tablet products correlates well with the biorelevant fasting conditions.
Conclusion: This research provides insights into the impact of key formulation variables on the in vitro QF release characteristics from HPMC matrix-based oral ER tablet formulations. Safe formulation design spaces were identified for LM QF ER tablet formulations across strengths to ensure dissolution similarity factor (f2) values compared to the respective RLD products are above 50. Moreover, we have demonstrated that compositionally disproportional QF HPMC matrix-based ER tablets can have similar in vitro dissolution profiles. Future studies will be focused on extending a similar QbD approach to additional strengths and identifying appropriate scaling factors for the development of additional strengths of oral ER tablet formulations that will demonstrate consistent bioavailability across strengths.
Acknowledgements: This project is supported by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of a grant (1U01FD007959). The contents are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement, by FDA/HHS, or the U.S. Government.
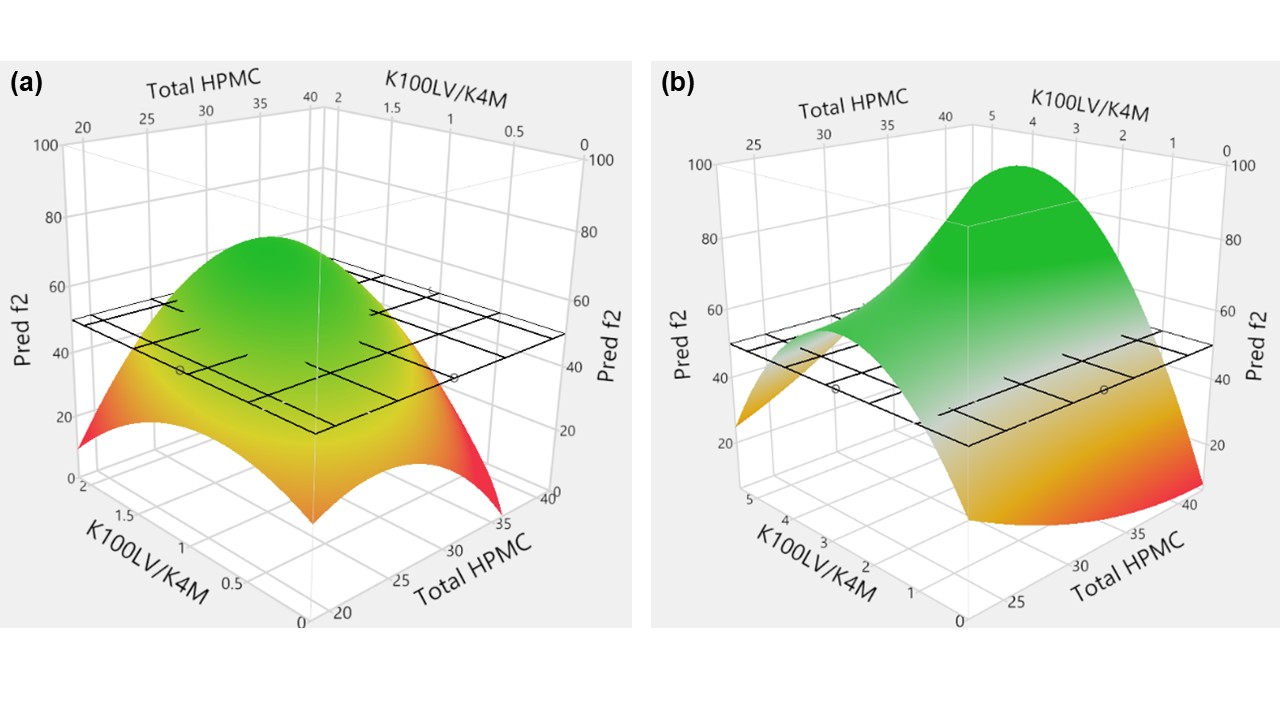 Figure 1. Response surface plots generated using JMP® to visualize the design space for (a) EQ 200 mg Base and (b) EQ 300 mg Base strength quetiapine fumarate extended-release tablet formulations. Formulation compositions with predicted similarity factor f2 (Y axis) ≥ 50 (Green zone above the grid surface) compared to the reference listed drug Seroquel XR® products were defined as the safe formulation design space. Two grades of HPMC K100LV and K4M were studied.
Figure 1. Response surface plots generated using JMP® to visualize the design space for (a) EQ 200 mg Base and (b) EQ 300 mg Base strength quetiapine fumarate extended-release tablet formulations. Formulation compositions with predicted similarity factor f2 (Y axis) ≥ 50 (Green zone above the grid surface) compared to the reference listed drug Seroquel XR® products were defined as the safe formulation design space. Two grades of HPMC K100LV and K4M were studied. 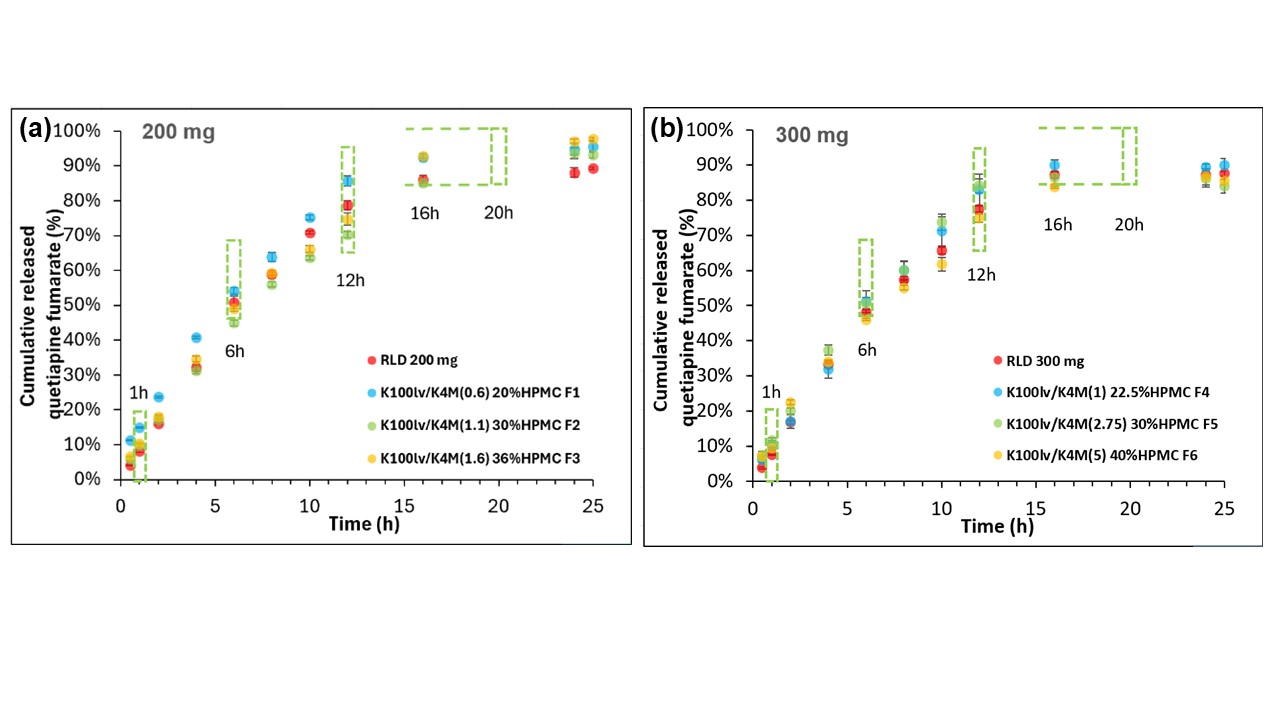 Figure 2. The in vitro dissolution profiles of LM QF ER tablet formulations across the 200 mg and 300 mg strengths obtained using USP apparatus 1 at 200 rpm (250 after 24 hr) with 20-mesh baskets in biphasic media (0.05 M citric acid and 0.09 N NaOH, pH 4.8 for first 5 hours followed by the addition of 100 mL of 0.05 M dibasic sodium phosphate dodecahydrate and 0.46 N NaOH to achieve a final pH of 6.6) (n=3, mean±SD). (a) EQ 200 mg Base strength: formulations F1 (K100LV/K4M ratio=0.6, 20% total HPMC), F2 (K100LV/K4M ratio=1.1, 30% total HPMC) and F3 (K100LV/K4M=1.6, 36% total HPMC) with f2 factors of 59.71, 64.97, and 53.70, compared to Seroquel XR® EQ 200 mg Base strength. (b) EQ 300 mg Base strength: formulations F4 (K100LV/K4M= 1, 22.5% total HPMC), F5 (K100LV/K4M= 2.75, 30% total HPMC) and F6 (K100LV/K4M=5, 40% total HPMC) with f2 factors of 71.79, 67.06, and 73.22, compared to Seroquel XR® EQ 300 mg Base strength. USP dissolution specifications (Test 1) for QF release are indicated by dashed green boxes.
Figure 2. The in vitro dissolution profiles of LM QF ER tablet formulations across the 200 mg and 300 mg strengths obtained using USP apparatus 1 at 200 rpm (250 after 24 hr) with 20-mesh baskets in biphasic media (0.05 M citric acid and 0.09 N NaOH, pH 4.8 for first 5 hours followed by the addition of 100 mL of 0.05 M dibasic sodium phosphate dodecahydrate and 0.46 N NaOH to achieve a final pH of 6.6) (n=3, mean±SD). (a) EQ 200 mg Base strength: formulations F1 (K100LV/K4M ratio=0.6, 20% total HPMC), F2 (K100LV/K4M ratio=1.1, 30% total HPMC) and F3 (K100LV/K4M=1.6, 36% total HPMC) with f2 factors of 59.71, 64.97, and 53.70, compared to Seroquel XR® EQ 200 mg Base strength. (b) EQ 300 mg Base strength: formulations F4 (K100LV/K4M= 1, 22.5% total HPMC), F5 (K100LV/K4M= 2.75, 30% total HPMC) and F6 (K100LV/K4M=5, 40% total HPMC) with f2 factors of 71.79, 67.06, and 73.22, compared to Seroquel XR® EQ 300 mg Base strength. USP dissolution specifications (Test 1) for QF release are indicated by dashed green boxes.