Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(W0930-08-53) AI/ML Model Informed Early-Stage Drug Development

Dineli T.S. T. S Ranathunga, Ph.D.
Scientist III, Research and Development
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Bend, Oregon, United States
Dineli T.S. T. S Ranathunga, Ph.D.
Scientist III, Research and Development
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Bend, Oregon, United States- TF
Thurman Falk, BS
Scientist III, Early Development
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Bend, Oregon, United States - TR
Tom A. Reynolds, Ph.D., Ph.D.
Manager, Research and Development
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Bend, Oregon, United States 
Nairuti Milan Mehta, MS
Scientist II, Research and Development
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Bend, Oregon, United States- TY
Thomas Yonker, BS, MBA
Vice President, Operations
Cerevance
Boston, Massachusetts, United States 
Sanjay Konagurthu, Ph.D.
Sr. Director, Science and Innovation
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Morrisville, North Carolina, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: Computational: The chemical structure and physicochemical properties of the poorly soluble CVN424 compound were initially evaluated. When experimental measured compound properties were unavailable, they were predicted computationally using in-house AI/ML models. All in-silico modeling such as quantum mechanical (QM), molecular dynamics (MD), and statistical modeling tools, along with AI/ML modeling were conducted using the Quadrant 2® program. As a first step, the Developability Classification System (DCS) was applied to categorize the drug based on its properties (Figure 1a). A systematic framework combining AI/ML and statistical modeling algorithms was then used to guide formulation technology selection. This framework evaluates critical drug characteristics—such as lipophilicity (Log P), pKa, partition coefficient, precipitation kinetics, solubility, melting point, dose, and thermal stability—to recommend optimal solubilization technologies aimed at improving solubility and bioavailability. Following these recommendations, additional in-silico studies were conducted to identify suitable excipients for the selected formulation strategies. Appropriate excipient selection is crucial for reducing the time and cost associated with empirical screening of the numerous excipients available on the market. A conformational distribution analysis of CVN424 was performed using high-level QM calculations. Advanced QSAR models, incorporating AI/ML algorithms, were used to generate molecular descriptors—such as hydrogen-bond donors/acceptors, and electrostatic potentials. These descriptors, alongside MD-derived molecular interaction energies, were used to analyze drug–excipient interactions. Comparative analyses against a broad excipient database allowed for the prediction of suitable polymeric dispersion excipients. Additionally, MD simulations at various drug loadings were conducted to evaluate how CVN424 disperses within the excipient matrix and the extent of drug–excipient interactions as a function of drug loading. The maximum feasible drug loading was calculated for each lead excipient. Experimental: Based on the in-silico modeling outputs and pre-formulation screening studies, several formulation approaches were selected to evaluate the feasibility of enhancing the oral bioavailability of CVN424. These included spray-dried intermediate (SDI) formulations with five polymers as well as nanomilled suspensions and suspension-based SDIs. Developed formulations were analyzed (using SEM, solvent spike, biorelevant two-stage dissolution performance, etc). Lead formulations were selected based on their physical characteristics, in-vitro performance, and physical and chemical stability. The scope of this abstract focuses exclusively on technology and formulation selection guided by in-silico modeling tools.
Results: The predicted formulation technologies suitable for enhancing the solubility of CVN-424 are presented in a stoplight display in Figure 1. In this display, green indicates a high likelihood of success, yellow indicates moderate likelihood, and red indicates “not likely to succeed”. Results are shown across 3 dose ranges to better inform technology selection, as the dose amount plays a critical role in formulation strategy—particularly in the early stages of development when exact dosing may not yet be known. For amorphous solid dispersion formulations, such as spray drying, the appropriate selection of dispersion excipients is essential to achieving a stable amorphous dispersion. Figures 2a shows the predicted list of polymeric dispersion excipients with favorable performance for CVN-424, along with their calculated maximum drug loadings. The dispersion behavior of CVN-424 within the excipient matrix, as well as the level of drug–excipient interaction as a function of drug loading (wt%), is illustrated through MD simulation snapshots in Figure 2b. These lead excipients and their associated maximum drug loadings are recommended for further evaluation in formulation development. Based on computational predictions, spray-dried formulations and nanomilled suspensions were selected. SDIs were manufactured using five polymers—HPMCAS-H, HPMCAS-M, HPMC E3LV, Eudragit L100, and Soluplus—selected based on recommendations from the in-silico modeling and pre-formulation screening experiments. Nanomilled suspensions of CVN-424 were developed and to isolate the nanomilled suspensions a spray drying process was further developed. Figure 3 illustrates the SEM results comparing the bulk CVN-424 API, one of the selected feasibility SDI formulations (25:75 CVN-424:Eudragit L100), nano Suspension (dried), and the nano-suspension SDIs.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the value of an integrated in-silico approach in guiding early-stage formulation development for poorly soluble drug compounds like CVN-424. By leveraging computational tools, the study identified suitable solubilization strategies and excipient candidates. These insights supported the selection of spray-dried and nanomilled formulations for further evaluation, streamlining the development process and reducing reliance on empirical trial-and-error. Overall, this approach underscores the potential of predictive modeling to accelerate formulation and drug development.
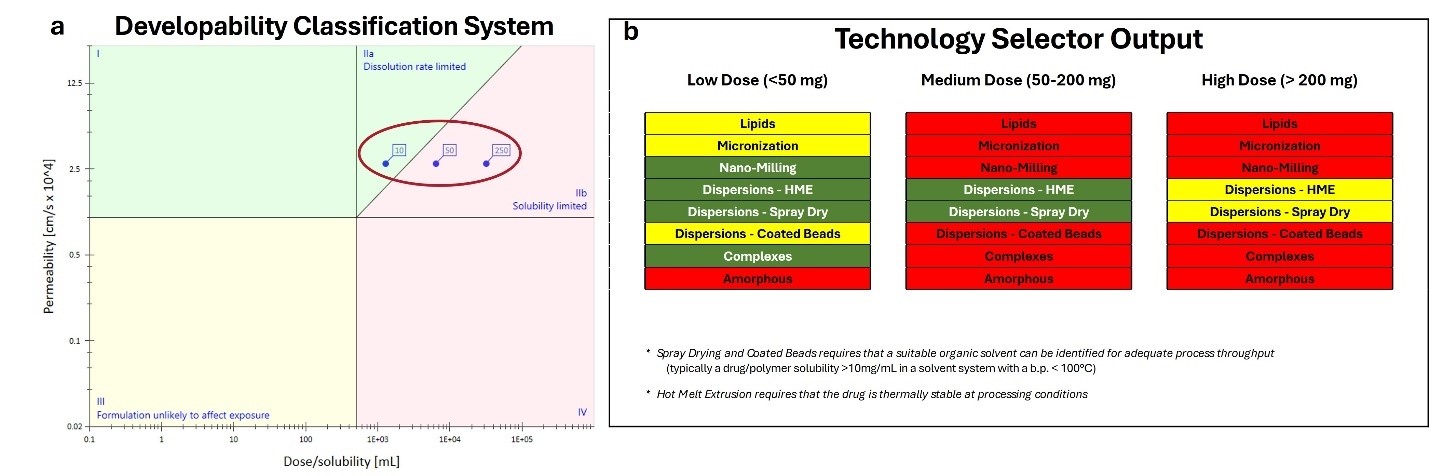 Figure 1: Computational modeling results. a) Developability Classification System, b) Predicted formulation technologies suitable for enhancing the solubility of the compound.
Figure 1: Computational modeling results. a) Developability Classification System, b) Predicted formulation technologies suitable for enhancing the solubility of the compound.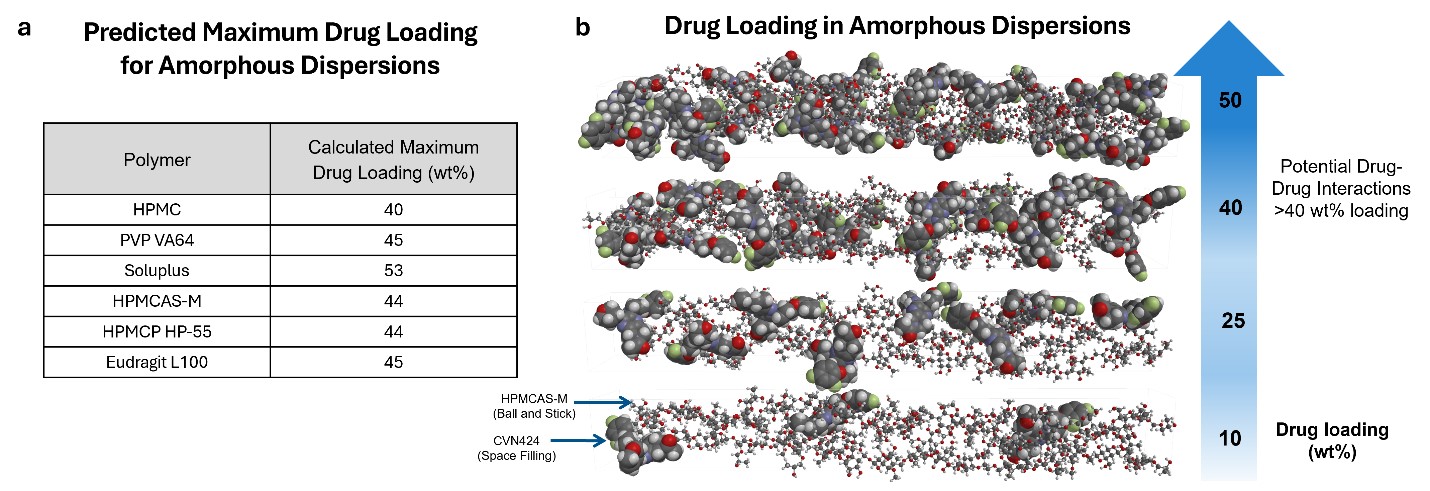 Figure 2: a) Predicted list of polymeric dispersion excipients with their calculated maximum drug loadings, b) MD simulation snapshots of CVN424:HPMCAS-M dispersions (HPMCAS-M shown as ball-and-stick, CVN424 as space-filling) illustrate drug–excipient interactions as a function of drug loading (wt%).
Figure 2: a) Predicted list of polymeric dispersion excipients with their calculated maximum drug loadings, b) MD simulation snapshots of CVN424:HPMCAS-M dispersions (HPMCAS-M shown as ball-and-stick, CVN424 as space-filling) illustrate drug–excipient interactions as a function of drug loading (wt%).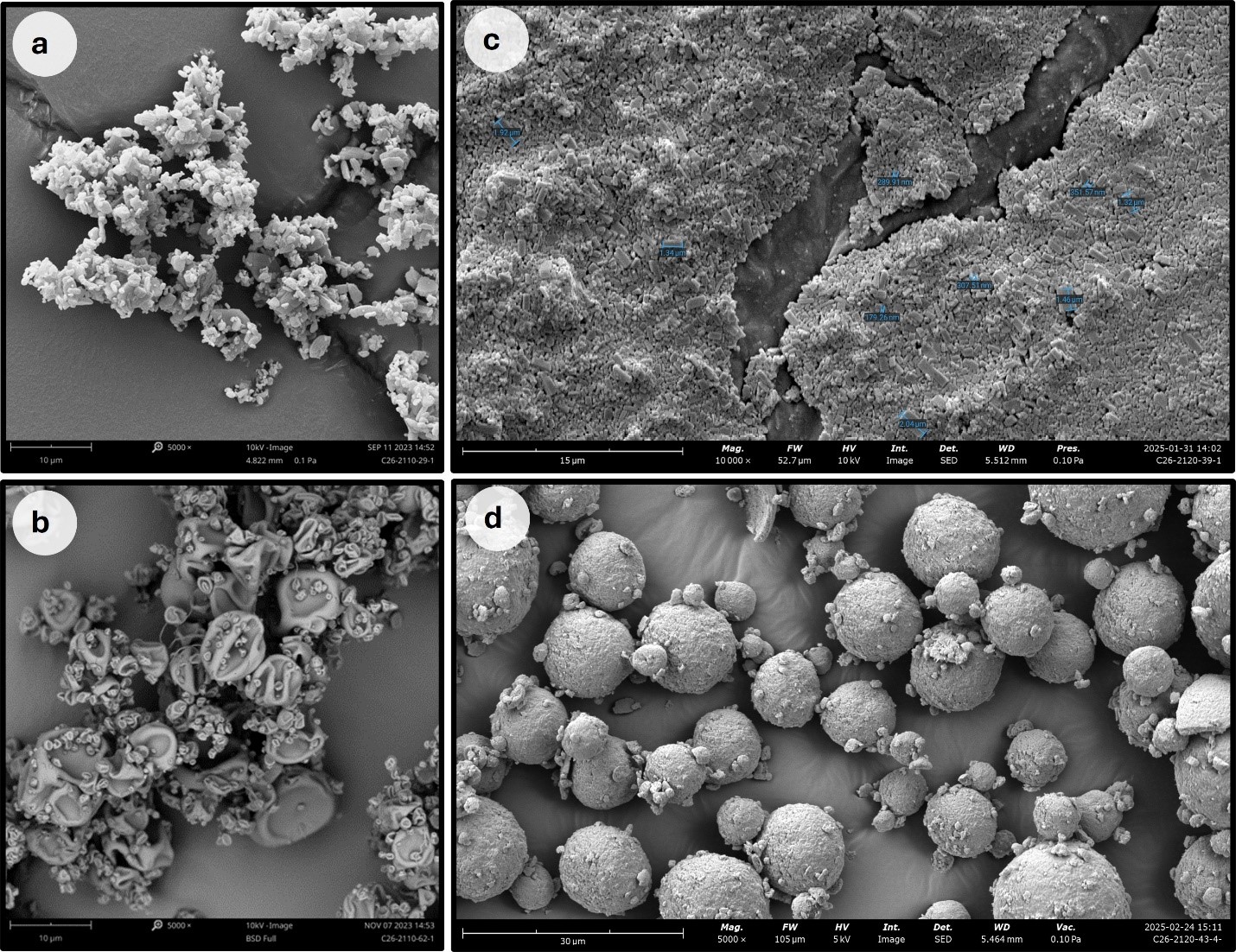 Figure 3: SEM images. a) SEM morphology of CVN-424 API captured at 5000x magnification. API morphology consists of platy crystals, most particles being less than 10 µm, b) SEM morphology of feasibility SDIs 25:75 CVN-424:Eudragit L100, c) SEM morphology of nano Suspension (dried). The morphology of the particles is columnar crystals. Observed particles range from 179 nm to 2.04 µm. d) SEM morphology of nano-suspension SDI. They are spherical and composed of aggregated nano crystals.
Figure 3: SEM images. a) SEM morphology of CVN-424 API captured at 5000x magnification. API morphology consists of platy crystals, most particles being less than 10 µm, b) SEM morphology of feasibility SDIs 25:75 CVN-424:Eudragit L100, c) SEM morphology of nano Suspension (dried). The morphology of the particles is columnar crystals. Observed particles range from 179 nm to 2.04 µm. d) SEM morphology of nano-suspension SDI. They are spherical and composed of aggregated nano crystals. 